Pooled Long-Term Outcomes With Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab or Nivolumab Alone in Patients With Advanced Melanoma
- PMID: 39504507
- PMCID: PMC11895829
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.24.00400
Pooled Long-Term Outcomes With Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab or Nivolumab Alone in Patients With Advanced Melanoma
Abstract
Purpose: Nivolumab (NIVO) + ipilimumab (IPI) combination and NIVO monotherapy have demonstrated durable clinical benefit in patients with unresectable/metastatic melanoma. This analysis describes long-term overall survival (OS) with the combination or monotherapy pooled across all major company-sponsored trials, as well as clinical factors associated with survival, in patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) treatment-naïve unresectable/metastatic melanoma.
Methods: Data were pooled from six CheckMate studies in ICI treatment-naïve patients receiving NIVO + IPI (NIVO 1 mg/kg + IPI 3 mg/kg or NIVO 3 mg/kg + IPI 1 mg/kg) or NIVO monotherapy (3 mg/kg). OS was assessed for each treatment, as well as in select subgroups. Cox proportional multivariate analysis (MVA) and classification and regression tree (CART) analyses were performed within treatment arms.
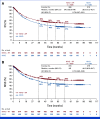
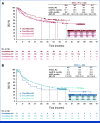
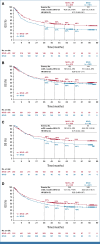
Results: Median follow-up for OS was 45.0 months for patients treated with NIVO + IPI (n = 839) and 35.8 months for patients treated with NIVO (n = 536). OS was longer with NIVO + IPI versus NIVO monotherapy (hazard ratio, 0.78 [95% CI, 0.67 to 0.91]), with 6-year OS rates of 52% versus 41%, respectively. Consistent benefit was observed in BRAF-mutant and BRAF-wild-type patients and those with normal and elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Numerical difference in OS was also observed across PD-L1 expression levels, although more pronounced with no/low PD-L1 expression. Clinical factors associated with decreased survival in both the MVA and CART analyses were LDH > upper limit of normal with either treatment, age ≥65 years with NIVO + IPI, and the presence of liver metastases with NIVO monotherapy.
Conclusion: In this large, pooled nonrandomized retrospective analysis, we observed that NIVO + IPI provides longer OS than NIVO in patients with ICI treatment-naïve advanced melanoma and identifies clinical factors that appear to be associated with survival for each treatment, which may assist with treatment decision making.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02714218 NCT01721772 NCT01844505 NCT01024231 NCT00730639 NCT01927419.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures
References
-
- Long GV, Swetter SM, Menzies AM, et al. Cutaneous melanoma. Lancet. 2023;402:485–502. - PubMed
-
- Dimitriou F, Hauschild A, Mehnert JM, et al. Double trouble: Immunotherapy doublets in melanoma-approved and novel combinations to optimize treatment in advanced melanoma. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2022;42:1–22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

