[Role of Abelson interactor 2 in progression and prognosis of gastric cancer and its regulatory mechanisms]
- PMID: 39505332
- PMCID: PMC11744083
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.09.04
[Role of Abelson interactor 2 in progression and prognosis of gastric cancer and its regulatory mechanisms]
Abstract
Objective: To explore the regulatory role of Abelson interactor 2 (ABI2) in progression and prognosis of gastric cancer.
Methods: TIMER2.0, GEPIA, Kaplan-Meier Plotter and DAVID databases were used to analyze ABI2 expression in pancancer and its association with the prognosis of gastric cancer. Gastric cancer and adjacent tissues from 120 patients undergoing radical gastrectomy in our hospital between January, 2016 and October, 2018 were examined for ABI2 expression and its correlation with disease progression and prognosis. MGC-803 cell models of ABI2 knockdown and overexpression were established for observing the changes in cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and the impact of ABI2 expression modulation on xenograft growth was evaluated in nude mice.
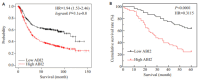
Results: Database analysis and examination of the clinical samples showed that ABI2 was highly expressed in gastric cancer tissues. Survival analysis suggested that gastric cancer patients with a high expression of ABI2 had a reduced postoperative 5-year survival rate (P < 0.0001), and further Cox univariate and multivariate survival analyses indicated that a high ABI2 expression was an independent risk factor affecting the patients survival outcomes (P=0.022, HR=1.887, 95% CI: 1.096-3.249). Enrichment analysis suggested the involvement of ABI2 in Wnt signaling. In MGC-803 cells, ABI2 overexpression promoted cell proliferation and xenograft growth in nude mice, increased the expressions of vimentin and N-cadherin, and lowered E-cadherin expression, while ABI2 knockdown produced the opposite effects. Mechanistic analysis revealed that ABI2 overexpression promoted the expressions of Wnt2 and β-catenin in both MGC-803 cells and the xenografts, and their expressions were significantly lowered by ABI2 knockdown.
Conclusion: ABI2 is highly expressed in gastric cancer, which affects long-term prognosis of the patients, possible due to its regulatory effect on Wnt signaling to promote proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells.
目的: 探讨Abelson相互作用因子2(ABI2)在胃癌进展和预后中的作用及机制。
方法: 通过TIMER2.0和GEPIA数据库分析ABI2在泛癌和胃癌中的表达,采用Kaplan-Meier Plotter数据库分析ABI2表达水平与胃癌预后的关系,通过DAVID数据库预测ABI2在生物系统中的功能。纳入在我院于2016年1月~2018年10月接受胃癌根治术治疗的120例胃癌患者,检测胃癌及癌旁组织中ABI2的表达水平,分析其与疾病进展的联系,并通过Cox单因素和多因素分析影响患者预后的危险因素。构建胃癌细胞系(MGC-803)ABI2干扰及过表达模型并构建裸鼠移植瘤模型,联合CCK-8、划痕、Transwell和免疫印迹实验分析ABI2对胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响。结合体内外研究分析ABI2影响胃癌细胞恶性生物学行为的可能分子机理。
结果: 生信分析和本院胃癌组织检测结果表明ABI2在胃癌组织中高表达(P < 0.05)。Kaplan-Meier Plotter数据库分析表明ABI2低表达患者的术后生存率优于高表达患者(P < 0.0001)。本院患者的生存分析结果显示,胃癌组织中ABI2高表达患者术后5年生存率降低(P < 0.0001),Cox单因素和多因素生存分析进一步表明,ABI2高表达是影响胃癌患者预后的独立危险因素(P=0.022,HR=1.887,95% CI:1.096~3.249)。富集分析提示,ABI2的作用可能与Wnt信号通路相关。上调ABI2促进裸鼠移植瘤和胃癌细胞的增殖能力(P < 0.05),并增加Vimentin和N-cadherin的表达,同时降低E-cadherin的表达(P < 0.05);下调ABI2则相反(P < 0.05)。机制分析发现上调ABI2促进移植瘤组织和胃癌细胞中Wnt2和β-catenin的表达(P < 0.05),下调ABI2则相反(P < 0.05)。
结论: ABI2在胃癌中表达升高并影响疾病远期预后,其可能与调控Wnt信号通路进而促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭能力有关。
Keywords: ABI2; Wnt signaling pathway; gastric cancer; invasion; migration; prognosis; proliferation.
Figures







References
-
- 郑 荣寿, 张 思维, 孙 可欣, et al. 2016年中国恶性肿瘤流行情况分析. 中华肿瘤杂志. 2023;45(3):212–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
