AS160 is a lipid-responsive regulator of cardiac Ca2+ homeostasis by controlling lysophosphatidylinositol metabolism and signaling
- PMID: 39505896
- PMCID: PMC11542008
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54031-5
AS160 is a lipid-responsive regulator of cardiac Ca2+ homeostasis by controlling lysophosphatidylinositol metabolism and signaling
Abstract
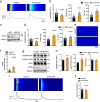
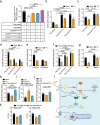
The obese heart undergoes metabolic remodeling and exhibits impaired calcium (Ca2+) homeostasis, which are two critical assaults leading to cardiac dysfunction. The molecular mechanisms underlying these alterations in obese heart are not well understood. Here, we show that the Rab-GTPase activating protein AS160 is a lipid-responsive regulator of Ca2+ homeostasis through governing lysophosphatidylinositol metabolism and signaling. Palmitic acid/high fat diet inhibits AS160 activity through phosphorylation by NEK6, which consequently activates its downstream target Rab8a. Inactivation of AS160 in cardiomyocytes elevates cytosolic Ca2+ that subsequently impairs cardiac contractility. Mechanistically, Rab8a downstream of AS160 interacts with DDHD1 to increase lysophosphatidylinositol metabolism and signaling that leads to Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Inactivation of NEK6 prevents inhibition of AS160 by palmitic acid/high fat diet, and alleviates cardiac dysfunction in high fat diet-fed mice. Together, our findings reveal a regulatory mechanism governing metabolic remodeling and Ca2+ homeostasis in obese heart, and have therapeutic implications to combat obesity cardiomyopathy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Insulin and AMPK regulate FA translocase/CD36 plasma membrane recruitment in cardiomyocytes via Rab GAP AS160 and Rab8a Rab GTPase.J Lipid Res. 2012 Apr;53(4):709-17. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M023424. Epub 2012 Feb 6. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22315395 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase pump is a major regulator of glucose transport in the healthy and diabetic heart.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1852(5):873-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.01.009. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25615793
-
Rab GTPase-activating protein AS160 is a major downstream effector of protein kinase B/Akt signaling in pancreatic beta-cells.Diabetes. 2008 May;57(5):1195-204. doi: 10.2337/db07-1469. Epub 2008 Feb 14. Diabetes. 2008. PMID: 18276765
-
Muscle cells engage Rab8A and myosin Vb in insulin-dependent GLUT4 translocation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008 Oct;295(4):C1016-25. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00277.2008. Epub 2008 Aug 13. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18701652
-
Altered sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium cycling--targets for heart failure therapy.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2012 Dec;9(12):717-33. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2012.145. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 23090087 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wong, C. & Marwick, T. H. Obesity cardiomyopathy: pathogenesis and pathophysiology. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med.4, 436–443 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Wong, C. & Marwick, T. H. Obesity cardiomyopathy: diagnosis and therapeutic implications. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med.4, 480–490 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Nakamura, M. & Sadoshima, J. Cardiomyopathy in obesity, insulin resistance and diabetes. J. Physiol.598, 2977–2993 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

