Identification of sentinel lymph node macrometastasis in breast cancer by deep learning based on clinicopathological characteristics
- PMID: 39505964
- PMCID: PMC11541545
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-78040-y
Identification of sentinel lymph node macrometastasis in breast cancer by deep learning based on clinicopathological characteristics
Abstract
The axillary lymph node status remains an important prognostic factor in breast cancer, and nodal staging using sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) is routine. Randomized clinical trials provide evidence supporting de-escalation of axillary surgery and omission of SLNB in patients at low risk. However, identifying sentinel lymph node macrometastases (macro-SLNMs) is crucial for planning treatment tailored to the individual patient. This study is the first to explore the capacity of deep learning (DL) models to identify macro-SLNMs based on preoperative clinicopathological characteristics. We trained and validated five multivariable models using a population-based cohort of 18,185 patients. DL models outperform logistic regression, with Transformer showing the strongest results, under the constraint that the sensitivity is no less than 90%, reflecting the sensitivity of SLNB. This highlights the feasibility of noninvasive macro-SLNM prediction using DL. Feature importance analysis revealed that patients with similar characteristics exhibited different nodal status predictions, indicating the need for additional predictors for further improvement.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Clinical decision support; Deep learning; Lymphatic metastasis; Sentinel lymph node.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
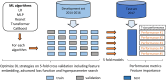
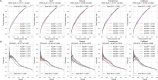
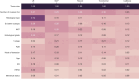

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

