Smad transcription factors as mediators of 7 transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor signalling
- PMID: 39506064
- PMCID: PMC11950520
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-024-01413-6
Smad transcription factors as mediators of 7 transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor signalling
Abstract
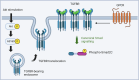
The Smad transcription factors are well known for their role at the core of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signalling. However, recent evidence shows that the Smad transcription factors play a vital role downstream of other classes of receptors including G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR). The versatility of Smad transcription factors originated from the two regions that can be differently activated by the TGF-β receptor superfamily or through the recruitment of intracellular kinases stimulated by other receptors classes such as GPCRs. The classic GPCR signalling cascade is further expanded to conditional adoption of the Smad transcription factor under the stimulation of Akt, demonstrating the unique involvement of the Smad transcription factor in GPCR signalling pathways in disease environments. In this review, we provide a summary of the signalling pathways of the Smad transcription factors as an important downstream mediator of GPCRs, presenting exciting opportunities for discovering new therapeutic targets for diseases.
Keywords: Akt; GPCR signalling; Smad; phospho-Smad; transactivation dependent; transforming growth factor-beta receptor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Derynck R, Zhang Y, Feng XH. Transcriptional activators of TGF-β responses: Smads. Cell. 1998;95:737–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

