The Systemic Immune Inflammation Index as a Novel Predictive Biomarker for Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Risk Following Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies
- PMID: 39506446
- PMCID: PMC12246735
- DOI: 10.2174/0115701611328810241028112700
The Systemic Immune Inflammation Index as a Novel Predictive Biomarker for Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Risk Following Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies
Abstract
Background: Contrast-induced Acute Kidney Injury (CI-AKI) frequently occurs as a complication following PCI, making the identification of high-risk patients challenging. While the systemic immune inflammation index (SII) might aid in predicting CI-AKI, the current evidence remains insufficient.
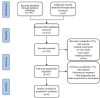
Methods: We conducted a systematic literature search using PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and the Cochrane Library, with a cut-off date of 3/20/2024. We included observational studies that examined the predictive value of SII for the risk of CI-AKI.
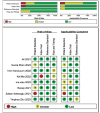
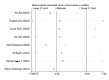
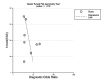
Results: This meta-analysis encompassed 8 studies with a combined total of 6301 participants. Results showed pooled sensitivity and specificity of 0.73 (95% CI 0.69-0.76) and 0.68 (95% CI 0.57- 0.77), respectively. The sROC curve analysis indicated an AUC of 0.74 (95% CI 0.70-0.78). The risk of publication bias was low (p = 0.18).
Conclusion: The results of this study suggest that SII has a relatively high sensitivity and could function as a biomarker for the prediction of CI-AKI risk in people receiving PCI treatment.
Keywords: Percutaneous coronary intervention; contrast-induced acute kidney; injury; meta-analysis.; prognosis; systemic immune inflammation index.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures





References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

