Novel function of single-target regulator NorR involved in swarming motility and biofilm formation revealed in Vibrio alginolyticus
- PMID: 39506750
- PMCID: PMC11542441
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-024-02057-y
Novel function of single-target regulator NorR involved in swarming motility and biofilm formation revealed in Vibrio alginolyticus
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Novel function of single-target regulator NorR involved in swarming motility and biofilm formation revealed in Vibrio alginolyticus.BMC Biol. 2024 Dec 16;22(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-02095-6. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39681855 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
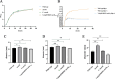
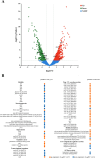
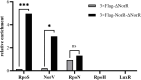
NorR, as a single-target regulator, has been demonstrated to be involved in NO detoxification in bacteria under anaerobic conditions. Here, the norR gene was identified and deleted in the genome of Vibrio alginolyticus. The results showed that deletion of norR in Vibrio alginolyticus led to lower swarming motility and more biofilm formation on aerobic condition. Moreover, we proved that NorR from E. coli had a similar function in controlling motility. NorR overexpression led to increased resistance to oxidative stress and tetracycline. We also observed a reduced ability of the NorR-overexpressing strain to adapt to iron limitation condition. Transcriptome analysis showed that the genes responsible for bacterial motility and biofilm formation were affected by NorR. The expressions of several sigma factors (RpoS, RpoN, and RpoH) and response regulators (LuxR and MarR) were also controlled by NorR. Furthermore, Chip-qPCR showed that there is a direct binding between NorR and the promoter of rpoS. Based on these results, NorR appears to be a central regulator involved in biofilm formation and swarming motility in Vibrio alginolyticus.
Keywords: Vibrio alginolyticus; Bacterial motility; Biofilm; NorR; Sigma factor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

