Understanding the role of CaCl2 in salt substitute for low-salt and high-quality surimi products
- PMID: 39507069
- PMCID: PMC11539108
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100877
Understanding the role of CaCl2 in salt substitute for low-salt and high-quality surimi products
Abstract
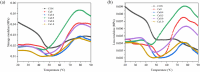
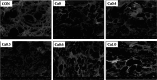
Salt substitute has been widely used to prepare low-salt foods due to potential health benefits, though the role of CaCl2 in salt substitute and its unique impacts on food quality have been rarely investigated. In this study, comprehensive research has been conducted to elucidate the effects of replacing NaCl with varying concentrations of CaCl2 on the surimi gel characteristics. The introduction of CaCl2 interacted with surimi proteins differently from NaCl, thus leading to difference in protein aggregation behaviors and surimi gel properties. It has been found that a proper proportion of CaCl2 for NaCl substitution could create salt bridges between surimi proteins more effectively, resulting in an ordered, smooth and dense gel network with an increased water holding capacity (WHC) and improved gel strength. Furthermore, TGase activated by Ca 2+ boosted the formation of ε-(γ-glutamyl) lysine bonds, which cross-linked surimi proteins to form a firm gel with a better three-dimensional structure. However, replacing NaCl with excessive amount of CaCl2 as divalent salts induced more serious protein aggregation, leading to water loss and gel properties deterioration. More specially, replacing NaCl with CaCl2 at 50% showed the best performance, as evidenced by the most abundant disulfide bonds and hydrophobic interactions, highest hardness and chewiness, and greatest storage modulus. This study provided new insights on developing high-quality surimi gels with significantly reduced salt concentration and improved gel characteristics.
Keywords: CaCl2; Gel properties; NaCl; Salt replacement; Surimi gel.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Barat J.M., Pérez-Esteve E., Aristoy M.C., Toldrá F. Partial replacement of sodium in meat and fish products by using magnesium salts. A review. Plant Soil. 2012;368(1–2):179–188.
-
- Brown K.H., Rivera J.A., Bhutta Z., Gibson R.A., King J.C., Lonnerdal B. Overview of zinc nutrition. Food Nutr. Bull. 2004;25(5):99–129. - PubMed
-
- Campo-Deaño L., Tovar C. The effect of egg albumen on the viscoelasticity of crab sticks made from Alaska Pollock and Pacific Whiting surimi. Food Hydrocolloids. 2009;23(7):1641–1646.
-
- Cao Y., Liang G., Li Z., Du D., Ma W., Dong X., Feng L., Zhang H., Liu Z. Effect of different concentrations of lysine on the transglutaminase-induced mixed surimi gel properties. Food Science of Animal Products. 2024;2(2)
-
- Chen N., Jiang Q., Gao P., Yu D., Yang F., Xu Y., Xia W. Gel properties, physicochemical properties, and sensory attributes of white leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) surimi gel treated with sodium chloride (NaCl) substitutes. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023;58(1):22–36.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

