Insulin Mediates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses and Oxidative Stress in BV2 Microglia
- PMID: 39507265
- PMCID: PMC11539848
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S481101
Insulin Mediates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses and Oxidative Stress in BV2 Microglia
Abstract
Introduction: Insulin, the key hormone for glucose regulation, has garnered attention for its role as an immune modulator. Impaired insulin signaling in the central nervous system is linked to neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Microglia, the resident macrophage-like immune cells in the brain, are key regulators of neuroinflammation. However, the mechanisms by which insulin influences microglial immune responses remain relatively unknown.
Methods: This study aimed to assess the effects of post-treatment with insulin [30 minutes after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) exposure] on LPS-induced inflammatory responses in BV2 microglial cells.
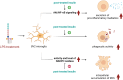
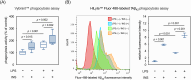
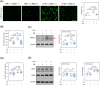
Results: Post-treatment with insulin potentiated LPS-induced production of nitric oxide and pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF and IL-6, through activation of the Akt/NF-κB pathway. Insulin also enhanced the ability of BV2 cells to phagocytose bacteria particles and β-amyloid fibrils. Conversely, insulin inhibited activation of NADPH oxidase and reduced intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species in LPS-treated BV2 cells.
Conclusion: Insulin enhances microglial immune competence when challenged by endotoxins but mitigates oxidative stress in these cells.
Keywords: p47phox; phagocytosis; superoxide dismutase; β-amyloid.
© 2024 Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

