Fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm applied in computed tomography images of patients with intracranial hemorrhage
- PMID: 39507424
- PMCID: PMC11537926
- DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2024.1440304
Fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm applied in computed tomography images of patients with intracranial hemorrhage
Abstract
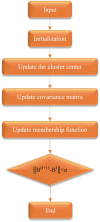
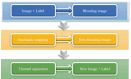
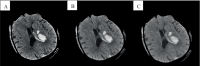
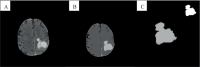
In recent years, intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) has garnered significant attention as a severe cerebrovascular disorder. To enhance the accuracy of ICH detection and segmentation, this study proposed an improved fuzzy C-means (FCM) algorithm and performed a comparative analysis with both traditional FCM and advanced convolutional neural network (CNN) algorithms. Experiments conducted on the publicly available CT-ICH dataset evaluated the performance of these three algorithms in predicting ICH volume. The results demonstrated that the improved FCM algorithm offered notable improvements in computational time and resource consumption compared to the traditional FCM algorithm, while also showing enhanced accuracy. However, it still lagged behind the CNN algorithm in areas such as feature extraction, model generalization, and the ability to handle complex image structures. The study concluded with a discussion of potential directions for further optimizing the FCM algorithm, aiming to bridge the performance gap with CNN algorithms and provide a reference for future research in medical image processing.
Keywords: computed tomography (CT) images; convolutional neural network (CNN); fuzzy C-means clustering (FCM) algorithm; image segmentation; intracranial hemorrhage (ICH).
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Song, Qiu, Ye and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Cajander S., Tina E., Bäckman A., Magnuson A., Strålin K., Söderquist B., et al. . (2016). Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction measurement of HLA-DRA gene expression in whole blood is highly reproducible and shows changes that reflect dynamic shifts in monocyte surface HLA-DR expression during the course of sepsis. PLoS One 11:e0154690. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154690, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Callejas-Moraga E. L., Casado E., Gomez-Nuñez M., Caresia-Aroztegui A. P. (2020). Severe osteomalacia with multiple insufficiency fractures secondary to intravenous iron therapy in a patient with Rendu-Osler-weber syndrome. Bone Rep 13:100712. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2020.100712, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheswick R., Cartmell E., Lee S., Upton A., Weir P., Moore G., et al. . (2019). Comparing flow cytometry with culture-based methods for microbial monitoring and as a diagnostic tool for assessing drinking water treatment processes. Environ. Int. 130:104893. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.06.003, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

