Risk factors for identifying pneumocystis pneumonia in pediatric patients
- PMID: 39507946
- PMCID: PMC11537976
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1398152
Risk factors for identifying pneumocystis pneumonia in pediatric patients
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to identify the risk factors and construct the diagnostic model associated with pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in pediatric patients.
Methods: This retrospective observational study analyzed 34 cases of PCP and 51 cases of other types of pneumonia treated at Children's Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University between January 2021 and August 2023. Multivariate binary logistic regression was used to identify the risk factors associated with PCP. Receiver operating characteristic curves and calibration plots were constructed to evaluate the diagnostic model.
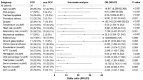
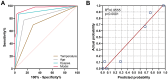
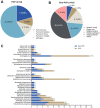
Results: Twenty clinical variables significantly differed between the PCP and non-PCP groups. Multivariate binary logistic regression analysis revealed that dyspnea, body temperature>36.5°C, and age<1.46 years old were risk factors for PCP. The area under the curve of the diagnostic model was 0.958, the P-value of Hosmer-Lemeshow calibration test was 0.346, the R2 of the calibration plot for the actual and predicted probability of PCP was 0.9555 (P<0.001), and the mean Brier score was 0.069. In addition, metagenomic next-generation sequencing revealed 79.41% (27/34) and 52.93% (28/53) mixed infections in the PCP and non-PCP groups, respectively. There was significantly more co-infection with cytomegalovirus and Streptococcus pneumoniae in the PCP group than that in the non-PCP group (p<0.05).
Conclusions: Dyspnea, body temperature>36.5°C, and age<1.46 years old were found to be independent risk factors for PCP in pediatric patients. The probability of co-infection with cytomegalovirus and S. pneumoniae in the PCP group was significantly higher than that in the non-PCP group.
Keywords: area under the curve; metagenomic next-generation sequencing; pediatric; pneumocystis pneumonia; receiver operating characteristic curve.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Li, Chen, Wang, Yang, Xu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chang C., Wang H., Zhang L., Hao J., Wang X., Wang Y., et al. (2023). Clinical efficiency of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in sputum for pathogen detection of patients with pneumonia according to disease severity and host immune status. Infect. Drug Resist. 16, 5869–5885. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S419892 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Donnelly J. P., Chen S. C., Kauffman C. A., Steinbach W. J., Baddley J. W., Verweij P. E., et al. (2020). Revision and update of the consensus definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European organization for research and treatment of cancer and the mycoses study group education and research consortium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 71, 1367–1376. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz1008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

