Clopidogrel ameliorates high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis in mice through activation of the AMPK signaling pathway and beyond
- PMID: 39508046
- PMCID: PMC11537861
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1496639
Clopidogrel ameliorates high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis in mice through activation of the AMPK signaling pathway and beyond
Abstract
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) frequently confers an increased risk of vascular thrombosis; however, the marketed antiplatelet drugs are investigated for the prevention and treatment of MASLD in patients with these coexisting diseases.
Methods: To determine whether clopidogrel could ameliorate high-fat diet (HFD)-induced hepatic steatosis in mice and how it works, mice were fed on normal diet or HFD alone or in combination with or without clopidogrel for 14 weeks, and primary mouse hepatocytes were treated with palmitate/oleate alone or in combination with the compounds examined for 24 h. Body weight, liver weight, insulin resistance, triglyceride and total cholesterol content in serum and liver, histological morphology, transcriptomic analysis of mouse liver, and multiple key MASLD-associated genes and proteins were measured, respectively.
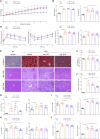
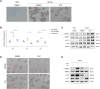
Results and discussion: Clopidogrel mitigated HFD-induced hepatic steatosis (as measured with oil red O staining and triglyceride kit assay) and reduced elevations in serum aminotransferases, liver weight, and the ratio of liver to body weight. Clopidogrel downregulated the expression of multiple critical lipogenic (Acaca/Acacb, Fasn, Scd1, Elovl6, Mogat1, Pparg, Cd36, and Fabp4), profibrotic (Col1a1, Col1a2, Col3a1, Col4a1, Acta2, and Mmp2), and proinflammatory (Ccl2, Cxcl2, Cxcl10, Il1a, Tlr4, and Nlrp3) genes, and enhanced phosphorylation of AMPK and ACC. However, compound C (an AMPK inhibitor) reversed enhanced phosphorylation of AMPK and ACC in clopidogrel-treated primary mouse hepatocytes and alleviated accumulation of intracellular lipids. We concluded that clopidogrel may prevent and/or reverse HFD-induced hepatic steatosis in mice, suggesting that clopidogrel could be repurposed to fight fatty liver in patients.
Keywords: AMPK; MASLD; NAFLD; clopidogrel; fatty liver; hepatic steatosis; steatotic liver.
Copyright © 2024 Tai, Shao, Zheng, Jiang, Han, Yin, Li, Ji, Mi, Yang, Feng, Duan and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Anonymous (2024). FDA approves first treatment for patients with liver scarring due to fatty liver disease. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-t... (Accessed August 16, 2024).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

