Shuxuening injection for treating acute ischemic stroke: a PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 39508047
- PMCID: PMC11538198
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1407669
Shuxuening injection for treating acute ischemic stroke: a PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
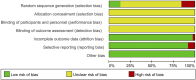
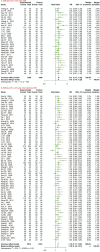
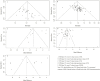
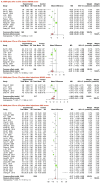
Background: Using Shuxuening injection (SXNI) for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is popular in China, but its efficacy and safety remain controversial. Purpose: This study aims to assess the efficacy and safety of SXNI as an add-on therapy for AIS. Study design: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Methods: We searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on SXNI for AIS in seven databases and two clinical trial registration platforms from their inception to January 2023. We used the Cochrane risk of bias tool to assess the methodological quality of the included studies and performed the meta-analysis with R software. The primary outcome was clinical efficacy, assessed by the clinical effective rate (CER). The secondary outcomes were neurological function, activities of daily living (ADL), and adverse events (AEs). Results: In total, 116 studies with 12,401 participants were included in this review. Fifteen (12.9%) studies were judged to be of moderate to high quality. SXNI plus conventional treatments (CTs) improved the CER compared with CTs alone (risk ratio [RR]: 1.21, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.17-1.25, p < 0.0001) or CTs plus other injections (RR: 1.18, 95% CI: 1.15-1.21, p < 0.0001). SXNI plus CTs reduced the National Institute of Health Stroke Scale score compared with CTs alone (mean difference [MD]: -4.00, 95% CI: -5.22 to -2.78, p < 0.0001) or CTs plus other injections (MD: -2.28, 95% CI: -3.41 to -1.16, p < 0.0001). SXNI plus CTs also decreased the Chinese Stroke Scale score compared with CTs alone (MD: -5.01, 95% CI: -7.38 to -2.65, p < 0.0001) or CTs plus other injections (MD: -4.31, 95% CI: -5.75 to -2.88, p < 0.0001). SXNI plus CTs was superior for increasing the Barthel index score compared with CTs alone (MD: 11.58, 95% CI: 8.27-14.90, p < 0.0001) or CTs plus other injections (MD: 5.43, 95% CI: 0.48-10.39, p = 0.0317). The level of evidence for each outcome was assessed as low to very low. The most common AEs of SXNI were cardiovascular system events, and all these AEs were mild. Conclusion: SXNI combined with CTs maybe better than CTs alone or CTs plus other injections for improving the clinical efficacy, neurological function, and ADL of AIS patients, with relatively reliable safety. However, due to the low quality of the included studies, more rigorously designed RCTs with large sample sizes should be conducted in the future.
Systematic review registration: www.crd.york.ac.uk, identifier (CRD42023418565).
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke; meta-analysis; shuxuening injection; systematic review; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2024 Zhan, Xu, Zhu, Liu, Chen and Zhan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bhatia R., Hill M. D., Shobha N., Menon B., Bal S., Kochar P., et al. (2010). Low rates of acute recanalization with intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in ischemic stroke: real-world experience and a call for action. Stroke 41 (10), 2254–2258. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.592535 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cai L. M., Jiang J. Z. (2012). Summary analysis of the efficacy of Shuxuening injection for acute cerebral infarction. Hebei Med. J. 34 (8), 1217–1219. 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2012.08.058 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

