The potential of natural products to inhibit abnormal aggregation of α-Synuclein in the treatment of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 39508052
- PMCID: PMC11537895
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1468850
The potential of natural products to inhibit abnormal aggregation of α-Synuclein in the treatment of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
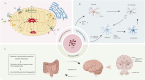
Parkinson's disease (PD), as a refractory neurological disorder with complex etiology, currently lacks effective therapeutic agents. Natural products (NPs), derived from plants, animals, or microbes, have shown promising effects in PD models through their antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as the enhancement of mitochondrial homeostasis and autophagy. The misfolding and deposition of α-Synuclein (α-Syn), due to abnormal overproduction and impaired clearance, being central to the death of dopamine (DA) neurons. Thus, inhibiting α-Syn misfolding and aggregation has become a critical focus in PD discovery. This review highlights NPs that can reduce α-Syn aggregation by preventing its overproduction and misfolding, emphasizing their potential as novel drugs or adjunctive therapies for PD treatment, thereby providing further insights for clinical translation.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; aggregation; misfolding; natural products; α-Synuclein.
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Lv, Zhao, Lai, Zheng, Qi, Zhao, Hu, Chen, Fu, Li, Xie, Wang, Wu and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
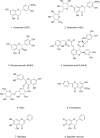
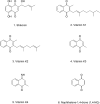

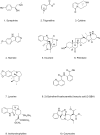
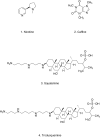
References
-
- Aliakbari F., Mohammad-Beigi H., Abbasi S., Rezaei-Ghaleh N., Lermyte F., Parsafar S., et al. (2021). Multiple protective roles of nanoliposome-incorporated baicalein against alpha-synuclein aggregates. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31 (7), 2007765. 10.1002/adfm.202007765 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

