Primary healthcare as a strategy for eliminating hepatitis C: the METRIC toolkit
- PMID: 39508085
- PMCID: PMC11569853
- DOI: 10.1017/S1463423624000355
Primary healthcare as a strategy for eliminating hepatitis C: the METRIC toolkit
Abstract
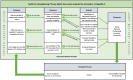
Aim: This paper presents the development of the METRIC toolkit, aimed at enhancing primary healthcare interventions in the context of hepatitis C control, thus contributing to the World Health Organization's global strategy to achieve the elimination of the disease by 2030.
Background: At the global level, most people living with hepatitis C are unaware of their condition. As such, the eradication of hepatitis C necessitates comprehensive strategies within primary healthcare settings, as it provides an opportunity to reach the general population, facilitates the identification of potential patients who may be unfamiliar with hepatitis C, and guides them toward adequate care. Herein, we propose the METRIC toolkit as a means to optimize the efficiency and efficacy of healthcare services dedicated to hepatitis C control.
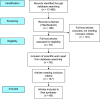
Methods: The development of the METRIC toolkit was guided by a thorough review of pertinent literature, focusing on primary healthcare interventions in hepatitis C control. Key components were identified, encompassing systematic problem identification, solution formulation, outcome evaluation, and feedback integration.
Findings: The METRIC toolkit represents a valuable resource for strengthening primary healthcare interventions in hepatitis C control. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and data-driven decision-making, this framework holds promise in advancing the global agenda towards hepatitis C elimination. However, its successful application requires careful consideration of contextual factors and ongoing adaptation to local needs and circumstances.
Keywords: general practitioners; hepatitis C; hepatitis C elimination; primary healthcare.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- AASLD-IDSA (2017) HCV testing and linkage to care. Recommendations for testing, managing, and treating Hepatitis C. HCV Guid. Available from: http://www.hcvguidelines.org/full-report/hcv-testing-and-linkage-care
-
- Bansal N, Gupta A, Sidhu TK, Maharishi RN, Gupta S and Roychoudhury AK (2023) Seroprevalence with epidemiological determinants of Hepatitis C virus and Treponema pallidum infection in blood donors of a teaching hospital in southwest Punjab, India: a 5-year study. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care 12(10), 2359–2365. 10.4103/JFMPC.JFMPC_490_23 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baptista-Leite R, Lopes H, Marinho RT and Peixe P (2014) Consenso Estratégico Nacional para a Hepatite C. Universidade Católica Editora, Lda. Available from: https://www.uceditora.ucp.pt/pt/consenso-estrategico-nacional/2453-conse...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials