The TOR signalling pathway in fungal phytopathogens: A target for plant disease control
- PMID: 39508186
- PMCID: PMC11541241
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.70024
The TOR signalling pathway in fungal phytopathogens: A target for plant disease control
Abstract
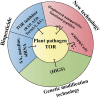
Plant diseases caused by fungal phytopathogens have led to significant economic losses in agriculture worldwide. The management of fungal diseases is mainly dependent on the application of fungicides, which are not suitable for sustainable agriculture, human health, and environmental safety. Thus, it is necessary to develop novel targets and green strategies to mitigate the losses caused by these pathogens. The target of rapamycin (TOR) complexes and key components of the TOR signalling pathway are evolutionally conserved in pathogens and closely related to the vegetative growth and pathogenicity. As indicated in recent systems, chemical, genetic, and genomic studies on the TOR signalling pathway, phytopathogens with TOR dysfunctions show severe growth defects and nonpathogenicity, which makes the TOR signalling pathway to be developed into an ideal candidate target for controlling plant disease. In this review, we comprehensively discuss the current knowledge on components of the TOR signalling pathway in microorganisms and the diverse roles of various plant TOR in response to plant pathogens. Furthermore, we analyse a range of disease management strategies that rely on the TOR signalling pathway, including genetic modification technologies and chemical controls. In the future, disease control strategies based on the TOR signalling network are expected to become a highly effective weapon for crop protection.
Keywords: TOR signalling pathway; disease control; plant pathogens.
© 2024 The Author(s). Molecular Plant Pathology published by British Society for Plant Pathology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicting interests.
Figures



References
-
- Ahn, C.S. , Lee, D.H. & Pai, H.S. (2019) Characterization of Maf1 in Arabidopsis: function under stress conditions and regulation by the TOR signaling pathway. Planta, 249, 527–542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022YFH0054/Sichuan Science and Technology Program
- 2023JDG0028/Sichuan Science and Technology Program
- 2023YFQ0100/Sichuan Science and Technology Program
- 2023ZYD0089/Sichuan Science and Technology Program
- 32300170/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- NASC2021PC04/the Local Financial Funds of Chengdu National Agricultural Science and Technology Center
- NASC2021ST08/the Local Financial Funds of Chengdu National Agricultural Science and Technology Center
- NASC2022KR07/the Local Financial Funds of Chengdu National Agricultural Science and Technology Center
- NASC2023TD08/the Local Financial Funds of Chengdu National Agricultural Science and Technology Center
- ZR2021QC200/Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- 34-IUA-02/the Science and Technology Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences
- Y2024QC33/Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund for Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

