Role of purinoreceptors in the release of extracellular vesicles and consequences on immune response and cancer progression
- PMID: 39510381
- PMCID: PMC12164022
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bj.2024.100805
Role of purinoreceptors in the release of extracellular vesicles and consequences on immune response and cancer progression
Abstract
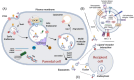
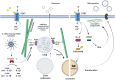
Cell-to-cell communication is a major process for accommodating cell functioning to changes in the environments and to preserve tissue and organism homeostasis. It is achieved by different mechanisms characterized by the origin of the message, the molecular nature of the messenger, its speed of action and its reach. Purinergic signalling is a powerful mechanism initiated by extracellular nucleotides, such as ATP, acting on plasma membrane purinoreceptors. Purinergic signalling is tightly controlled in time and space by the action of ectonucleotidases. Recent studies have highlighted the critical role of purinergic signalling in controlling the generation, release and fate of extracellular vesicles and, in this way, mediating long-distance responses. Most of these discoveries have been made in immune and cancer cells. This review is aimed at establishing the current knowledge on the way which purinoreceptors control extracellular vesicle-mediated communications and consequences for recipient cells.
Keywords: Cancer; Exosomes; Extracellular vesicles; Immune response; Purinoreceptors.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Burnstock G, Fredholm BB, North RA, Verkhratsky A. The birth and postnatal development of purinergic signalling. Acta Physiol. 2010;199:93–147. - PubMed
-
- Vultaggio-Poma V, Falzoni S, Salvi G, Giuliani AL, Di Virgilio F. Signalling by extracellular nucleotides in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2022;1869 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

