Structural insights into the agonist selectivity of the adenosine A3 receptor
- PMID: 39511145
- PMCID: PMC11544091
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53473-1
Structural insights into the agonist selectivity of the adenosine A3 receptor
Abstract
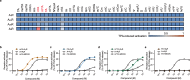
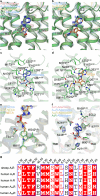
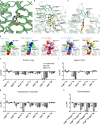
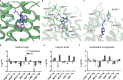
Adenosine receptors play pivotal roles in physiological processes. Adenosine A3 receptor (A3R), the most recently identified adenosine receptor, is expressed in various tissues, exhibiting important roles in neuron, heart, and immune cells, and is often overexpressed in tumors, highlighting the therapeutic potential of A3R-selective agents. Recently, we identified RNA-derived N6-methyladenosine (m6A) as an endogenous agonist for A3R, suggesting the relationship between RNA-derived modified adenosine and A3R. Despite extensive studies on the other adenosine receptors, the selectivity mechanism of A3R, especially for A3R-selective agonists such as m6A and namodenoson, remained elusive. Here, we identify tRNA-derived N6-isopentenyl adenosine (i6A) as an A3R-selective ligand via screening of modified nucleosides against the adenosine receptors. Like m6A, i6A is found in the human body and may be an endogenous A3R ligand. Our cryo-EM analyses elucidate the A3R-Gi complexes bound to adenosine, 5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (NECA), m6A, i6A, and namodenoson at overall resolutions of 3.27 Å (adenosine), 2.86 Å (NECA), 3.19 Å (m6A), 3.28 Å (i6A), and 3.20 Å (namodenoson), suggesting the selectivity and activation mechanism of A3R. We further conduct structure-guided engineering of m6A-insensitive A3R, which may aid future research targeting m6A and A3R, providing a molecular basis for future drug discovery.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
O.N. is a co-founder and an external director of Curreio, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural Characterization of Agonist Binding to an A3 Adenosine Receptor through Biomolecular Simulations and Mutagenesis Experiments.J Med Chem. 2019 Oct 10;62(19):8831-8846. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01164. Epub 2019 Sep 27. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31502843
-
Different efficacy of adenosine and NECA derivatives at the human A3 adenosine receptor: insight into the receptor activation switch.Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Jan 15;87(2):321-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.10.011. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24161786
-
Photomodulation of G protein-coupled adenosine receptors by a novel light-switchable ligand.Bioconjug Chem. 2014 Oct 15;25(10):1847-54. doi: 10.1021/bc5003373. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Bioconjug Chem. 2014. PMID: 25248077 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Probing and Molecular Modeling of the A₃ Adenosine Receptor: A Focus on Agonist Binding.Molecules. 2017 Mar 11;22(3):449. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030449. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28287473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Highly Selective A3 Adenosine Receptor Ligands in the Central and Peripheral Nervous System.Molecules. 2022 Mar 15;27(6):1890. doi: 10.3390/molecules27061890. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35335254 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress of CD73-adenosine signaling regulating hepatocellular carcinoma through tumor microenvironment.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 May 26;44(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03416-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40420185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular basis of ligand binding and receptor activation at the human A3 adenosine receptor.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 18;16(1):7674. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62872-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40825947
References
-
- Borea, P. A., Gessi, S., Merighi, S., Vincenzi, F. & Varani, K. Pharmacology of adenosine receptors: the state of the art. Physiol. Rev.98, 1591–1625 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

