Targeting protein homeostasis with small molecules as a strategy for the development of pan-coronavirus antiviral therapies
- PMID: 39511285
- PMCID: PMC11543989
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-07143-z
Targeting protein homeostasis with small molecules as a strategy for the development of pan-coronavirus antiviral therapies
Abstract
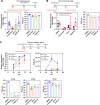
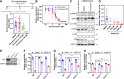
The COVID-19 pandemic has created a global health crisis, with challenges arising from the ongoing evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, the emergence of new strains, and the long-term effects of COVID-19. Aiming to overcome the development of viral resistance, our study here focused on developing broad-spectrum pan-coronavirus antiviral therapies by targeting host protein quality control mechanisms essential for viral replication. Screening an in-house compound library led to the discovery of three candidate compounds targeting cellular proteostasis. The three compounds are (1) the nucleotide analog cordycepin, (2) a benzothiozole analog, and (3) an acyldepsipeptide analog initially developed as part of a campaign to target the mitochondrial ClpP protease. These compounds demonstrated dose-dependent efficacy against multiple coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2, effectively inhibiting viral replication in vitro as well as in lung organoids. Notably, the compounds also showed efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 delta and omicron strains. As part of this work, we developed a BSL2-level cell-integrated SARS-CoV-2 replicon, which could serve as a valuable tool for high-throughput screening and studying intracellular viral replication. Our study should aid in the advancement of antiviral drug development efforts.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. World Health Organization (2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

