Understanding the heterogeneity and dysfunction of HDL in chronic kidney disease: insights from recent reviews
- PMID: 39511510
- PMCID: PMC11542271
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-024-03808-3
Understanding the heterogeneity and dysfunction of HDL in chronic kidney disease: insights from recent reviews
Abstract
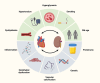
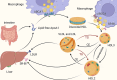
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a complex disease that affects the global population's health, with dyslipidemia being one of its major complications. High density lipoprotein (HDL) is regarded as the "hero" in the bloodstream due to its role in reverse cholesterol transport, which lowers cholesterol levels in the blood and prevents atherosclerosis. However, in the complex internal environment of CKD, even this "hero" may struggle to perform its beneficial functions and could potentially become harmful. This article reviews HDL heterogeneity, HDL subclasses, functional changes in HDL during the progression of CKD, and the application of HDL in CKD treatment. This review aims to deepen understanding of lipid metabolism abnormalities in CKD patients and provide a basis for new therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Dyslipidemia; High density lipoproteins; Subclasses.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Inker LA, Astor BC, Fox CH, Isakova T, Lash JP, Peralta CA, et al. KDOQI us commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 2014;63:713–35. 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.01.416. - PubMed
-
- Thomas MC, Cooper ME, Zimmet P. Changing epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and associated chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016;12(2):73–81. 10.1038/nrneph.2015.173. - PubMed
-
- Navaneethan SD, Zoungas S, Caramori ML, Chan JCN, Heerspink HJL, Hurst C, et al. Diabetes management in chronic kidney disease: Synopsis of the KDIGO 2022 clinical practice Guideline Update. Ann Intern Med. 2023;176(3):381–7. 10.7326/M22-2904. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

