Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: current treatment advances, emerging targeted therapy and underlying mechanisms
- PMID: 39511607
- PMCID: PMC11542428
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-024-01621-x
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: current treatment advances, emerging targeted therapy and underlying mechanisms
Abstract
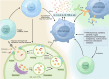
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a rapidly progressing, life-threatening syndrome characterized by excessive immune activation, often presenting as a complex cytokine storm. This hyperactive immune response can lead to multi-organ failure and systemic damage, resulting in an extremely short survival period if left untreated. Over the past decades, although HLH has garnered increasing attention from researchers, there have been few advancements in its treatment. The cytokine storm plays a crucial role in the treatment of HLH. Investigating the detailed mechanisms behind cytokine storms offers insights into targeted therapeutic approaches, potentially aiding in early intervention and improving the clinical outcome of HLH patients. To date, there is only one targeted therapy, emapalumab targeting interferon-γ, that has gained approval for primary HLH. This review aims to summarize the current treatment advances, emerging targeted therapeutics and underlying mechanisms of HLH, highlighting its newly discovered targets potentially involved in cytokine storms, which are expected to drive the development of novel treatments and offer fresh perspectives for future studies. Besides, multi-targeted combination therapy may be essential for disease control, but further trials are required to determine the optimal treatment mode for HLH.
Keywords: Cytokine storm; Emapalumab; Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; Pathogenic mechanisms; Targeted therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- La Rosée P, et al. Recommendations for the management of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults. Blood. 2019;133:2465–77. 10.1182/blood.2018894618. - PubMed
-
- Scott RB, Robb-Smith A. Histiocytic medullary reticulosis. The Lancet. 1939;234:194–8.
-
- Stepp SE, et al. Perforin gene defects in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Science. 1999;286:1957–9. 10.1126/science.286.5446.1957. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

