Mutation in Prkra results in cerebellar abnormality and reduced eIF2α phosphorylation in a model of DYT-PRKRA
- PMID: 39512178
- PMCID: PMC11625895
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.050929
Mutation in Prkra results in cerebellar abnormality and reduced eIF2α phosphorylation in a model of DYT-PRKRA
Abstract
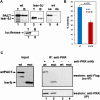
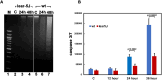
Variants in the PRKRA gene, which encodes PACT, cause the early-onset primary dystonia DYT-PRKRA, a movement disorder associated with disruption of coordinated muscle movements. PACT and its murine homolog RAX activate protein kinase R (PKR; also known as EIF2AK2) by a direct interaction in response to cellular stressors to mediate phosphorylation of the α subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2α). Mice homozygous for a naturally arisen, recessively inherited frameshift mutation, Prkralear-5J, exhibit progressive dystonia. In the present study, we investigated the biochemical and developmental consequences of the Prkralear-5J mutation. Our results indicated that the truncated PACT/RAX protein retains its ability to interact with PKR but inhibits PKR activation. Mice homozygous for the mutation showed abnormalities in cerebellar development as well as a severe lack of dendritic arborization of Purkinje neurons. Additionally, reduced eIF2α phosphorylation was noted in the cerebellum and Purkinje neurons of the homozygous Prkralear-5J mice. These findings indicate that PACT/RAX-mediated regulation of PKR activity and eIF2α phosphorylation plays a role in cerebellar development and contributes to the dystonia phenotype resulting from the Prkralear-5J mutation.
Keywords: Cerebellum; DYT-PRKRA; Dystonia; EIF2AK2; PACT/RAX; PKR.
© 2024. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures






Update of
-
A frameshift mutation in the murine Prkra gene causes dystonia and exhibits abnormal cerebellar development and reduced eIF2α phosphorylation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 4:2024.06.04.597421. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.04.597421. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Dis Model Mech. 2024 Nov 1;17(11):dmm050929. doi: 10.1242/dmm.050929. PMID: 38895245 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Beauvais, G., Rodriguez-Losada, N., Ying, L., Zakirova, Z., Watson, J. L., Readhead, B., Gadue, P., French, D. L., Ehrlich, M. E. and Gonzalez-Alegre, P. (2018). Exploring the interaction between eIF2alpha dysregulation, acute endoplasmic reticulum stress and DYT1 dystonia in the mammalian brain. Neuroscience 371, 455-468. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.12.033 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ASPIRE/Office of the Vice President for Research, University of South Carolina
- SPARC/Office of the Vice President for Research, University of South Carolina
- University of South Carolina
- Office of the Vice President for Research, University of South Carolina
- U01 DE020052/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

