An updated systematic review of pharmacological treatments for presbyopia
- PMID: 39512930
- PMCID: PMC11541684
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aopr.2024.09.001
An updated systematic review of pharmacological treatments for presbyopia
Abstract
Background: Presbyopia, a common age-related condition affecting near vision, impacts over a billion people worldwide. The aim of this paper is to review the main reports and results of clinical trials, comparing the newest pharmacological treatment options for presbyopia, their mechanisms of action, and possible side effects.
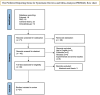
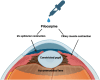
Main text: Pharmacological approaches, involving eye drops that target the underlying mechanisms of presbyopia, have gained growing interest. Two key pharmacological agents in this field are miotics and lens softeners. Miotics enhance near vision temporarily by creating a pinhole effect, though they may cause side effects and are under further investigation for long-term use with ongoing research also exploring the potential benefits of combining them with other drugs to improve outcomes and reduce adverse reactions. Lens softeners, on the other hand, aim to restore the flexibility of the lens, addressing one of the primary causes of presbyopia. Despite early trials, further development of lens softeners has been suspended. A notable advancement in this field is the recent FDA approval of 1.25% and 0.4% pilocarpine, a miotic agent, for presbyopia treatment. This milestone highlights the growing interest in pharmacological solutions for presbyopia, with several new drugs and their combinations currently being investigated for potential FDA approval.
Conclusions: pharmacological treatments, particularly miotics like pilocarpine, represent a promising alternative to conventional methods for managing presbyopia. Continued research into these treatments, especially combinations of drugs, may offer more effective and convenient options for presbyopia patients in the future.
Keywords: Medical; Pharmacological presbyopia treatment; Presbyopia; Presbyopia treatment.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological Treatment in Presbyopia.J Clin Med. 2022 Mar 3;11(5):1385. doi: 10.3390/jcm11051385. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35268476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Living with presbyopia: experiences from a virtual roundtable dialogue among impacted individuals and healthcare professionals.BMC Ophthalmol. 2022 May 5;22(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02432-9. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35513787 Free PMC article.
-
Pilocarpine in the Treatment of Presbyopia: Progress, Issues, and Future Prospects.Drugs Aging. 2024 Nov;41(11):897-906. doi: 10.1007/s40266-024-01155-4. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Drugs Aging. 2024. PMID: 39455529 Review.
-
Pharmacological treatments for the correction of presbyopia.Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol (Engl Ed). 2024 Aug;99(8):331-339. doi: 10.1016/j.oftale.2024.04.008. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol (Engl Ed). 2024. PMID: 38663714 Review.
-
Pilocarpine 1.25% and the changing landscape of presbyopia treatment.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2022 Jul 1;33(4):269-274. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000864. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35779051 Review.
References
-
- Vuity - pilocarpine ophthalmic solution for presbyopia. Med Lett Drugs Ther. Feb. 2022;64(1643):17–18. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources