The Link Between Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- PMID: 39512967
- PMCID: PMC11542734
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.71095
The Link Between Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Abstract
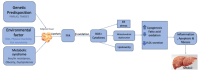
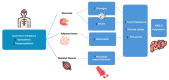
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), formerly nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) are prevalent chronic conditions with escalating global incidence. This study delves into the intricate interplay between MASLD and GERD. The primary objective is to comprehensively explore the association between MASLD and GERD, investigating how various factors contribute to the coexistence and potential exacerbation of these conditions. We conducted a literature search in PubMed and Google Scholar of only human studies over the past 10 years. The search included systematic review, meta-analysis, editorial, and cross-sectional studies of patients with MASLD and GERD. The prevalence of GERD in patients with MASLD was higher, with various risk factors coming into play. Obesity was identified as an independent risk factor for both GERD and MASLD. However, obese patients predominantly had higher disease progression. Lifestyle factors like physical activity and dietary modifications emerge as promising strategies to mitigate risk.
Keywords: bmi; gerd; masld; obesity; risk factor.
Copyright © 2024, Dutta et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
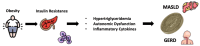
References
-
- A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: an international expert consensus statement. Eslam M, Newsome PN, Sarin SK, et al. J Hepatol. 2020;73:202–209. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
