Pyrroloquinoline Quinone (PQQ): Its impact on human health and potential benefits: PQQ: Human health impacts and benefits
- PMID: 39513102
- PMCID: PMC11541945
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100889
Pyrroloquinoline Quinone (PQQ): Its impact on human health and potential benefits: PQQ: Human health impacts and benefits
Abstract
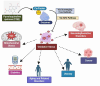
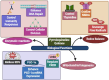
Pyrroloquinoline Quinone (PQQ) is a redox-active quinone molecule with significant implications for human health. Originally identified as a bacterial cofactor, PQQ has since been lauded for its diverse biological and therapeutic activities. It serves as an essential cofactor for oxidative enzymes that are vital for mitochondrial function and ATP synthesis. PQQ exhibits superior antioxidant properties that protect against ROS-mediated oxidative stress, aging, neurodegenerative diseases, certain cancers, diabetes, and metabolic disorders. It also enhances cognitive abilities and reduces insulin sensitivity. PQQ's antioxidant nature helps mitigate oxidative stress, which is implicated in many diseases. It has been shown to target cancer cells selectively, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic agent. Clinical studies have indicated the potential benefits of PQQ supplementation, including improvements in cardiovascular health, cognitive function, weight management, insulin sensitivity, and the prevention of metabolic syndromes. The safety of PQQ has been established, with no reported toxicity or genotoxicity in various studies, and it is considered a safe nutritional supplement. Future research directions should focus on determining the optimal dosages of PQQ for specific health outcomes and assessing its long-term effectiveness and safety. The translation of PQQ research into clinical practice could offer new strategies for managing metabolic disorders, enhancing cognitive health, and potentially extending lifespan. In summary, PQQ is a promising molecule with broad potential health benefits, impacting human health from cellular metabolism to disease prevention and treatment, positioning it as a key player in nutritional science and public health.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Cardiovascular health; Cellular metabolism; Metabolic disorders; Neuroprotection; Pyrroloquinoline quinone.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no financial or other relationships that might lead to a conflict of interest of the present article. All authors have reviewed the final version of the manuscript and approved it for publication.
Figures



References
-
- Ameyama M., Shinagawa E., Matsushita K., Adachi O. Growth stimulating substance for microorganisms produced by Escherichia coli causing the reduction of the lag phase in microbial growth and identity of the substance with pyrroloquinoline quinone. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1984;48(12):3099–3107. doi: 10.1080/00021369.1984.10866645. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

