Burden of hepatitis B in asymptomatic blood donor population of India: A systematic review & meta-analysis
- PMID: 39513206
- PMCID: PMC11544571
- DOI: 10.25259/ijmr_285_24
Burden of hepatitis B in asymptomatic blood donor population of India: A systematic review & meta-analysis
Abstract
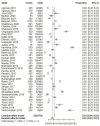
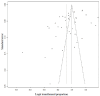
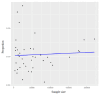
Background & objectives India has been classified as an intermediate Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) endemic country, and the transmission is believed to mostly occur horizontally. However, community-based data on HBV prevalence among blood donors in India are limited. The burden of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) is unknown in the asymptomatic blood donor population. We therefore conducted a meta-analysis to assess the prevalence of the HBV among the blood donor population in India. Methods We searched different databases for research articles on the prevalence of HBV in the blood donor population from India. Following the PRISMA guidelines, forty articles published between January 2013 and October 20, 2023, were selected for meta-analysis after removing duplicates and conducting a two-level screening process. Review Manager Version 5.3 (Rev Man 5.4) was used for statistical meta-analysis. The study has been registered with PROSPERO (number CRD42023487616). Results Forty articles were selected out of the 527 published manuscripts for meta-analysis, and a total of 22,22,736 blood donations were studied. Of these, 24,151 individuals (1.11%) were identified either as chronically infected with HBV or living with HBV infection. A pooled prevalence of approximately 1.11 per cent with a 95% confidence interval (CI) of (0.011; 0.0112) (common effect model) or 95% CI of (0.0079; 0.0116) (random effects model) was estimated. The included studies exhibited a high level of heterogeneity, probably due to different diagnostic approaches followed in different studies. Interpretation & conclusions The burden of hepatitis is profound, impacting public health, economies, and societies in India. The outcome of this study would help address such a burden and develop comprehensive strategies focused on prevention, early diagnosis, treatment, and necessary collaboration to achieve significant reductions in hepatitis-related morbidity and mortality.
Keywords: Blood donors; blood transfusion; disease burden; hepatitis B virus; hepatitis C prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- National Viral Hepatitis Control Program, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India National Viral Hepatitis Control Program. Available from: https://nvhcp.mohfw.gov.in/about_us, accessed on August 24, 2024.
-
- Agarwal N, Chatterjee K, Coshic P, Borgohain M. Nucleic acid testing for blood banks: An experience from a tertiary care centre in New Delhi, India. Transfus Apher Sci. 2013;49:482–4. - PubMed
-
- Arcot PJ, Pandey HC, Coshic P, Jain P, Kumar S, Chakroborty S. Comparative evaluation of ADVIA Centaur® XP chemiluminescence system for screening of HBV, HCV, HIV and syphilis in Indian blood donors. Transfus Apher Sci. 2022;61:103318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

