Baicalein suppresses inflammation and attenuates acute lung injury by inhibiting glycolysis via HIF‑1α signaling
- PMID: 39513601
- PMCID: PMC11564906
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13383
Baicalein suppresses inflammation and attenuates acute lung injury by inhibiting glycolysis via HIF‑1α signaling
Abstract
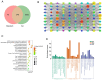
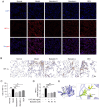
Baicalein, a flavonoid monomer compound isolated from the dried root of the traditional Chinese herb Scutellaria baicalensis, has several pharmacological activities, such as anti‑inflammatory, anti‑angiogenic, antitumor, antimicrobial and antiviral properties. Acute lung injury (ALI) is characterized by injury of the alveolar epithelium and capillary endothelium, which results in decreased lung volume, decreased lung compliance, ventilation/perfusion mismatch, intrapulmonary edema, alveolar edema and even acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of baicalein on lung injury and inflammation. Bioinformatics analysis using network pharmacology predicted that the hypoxia inducible factor‑1α (HIF‑1α) and glycolysis signaling pathways were involved in the mechanism underlying the therapeutic effects of baicalein. Further in vitro and in vivo experiments, such as immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence and PCR, verified that baicalein could inhibit HIF‑1α signaling, thus suppressing glycolysis, and improving inflammatory responses and ALI. Taken together, the results of the present study suggested that the anti‑inflammatory effects of baicalein on treating ALI were associated with its ability to suppress glycolysis via the HIF‑1α signaling pathway.
Keywords: HIF‑1α signaling; acute lung injury; baicalein; glycolysis; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Baicalein suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by regulating Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission of macrophages.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Jan;145:112408. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112408. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 34801855
-
Baicalein, an active component of Scutellaria baicalensis, protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Apr 11;153(1):197-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.02.010. Epub 2014 Feb 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24534526
-
Functional mechanism of baicalein in alleviating severe acute pancreatitis-acute lung injury by blocking the TLR4/MyD88/TRIF signaling pathway.Histol Histopathol. 2024 Oct;39(10):1381-1394. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-733. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 38557861
-
Baicalein exerts beneficial effects in lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammation by modulating macrophage polarization and inhibiting pyroptosis.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2024 Jan-Dec;43:9603271241249990. doi: 10.1177/09603271241249990. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38664950
-
Hypoxia signaling during acute lung injury.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015 Nov 15;119(10):1157-63. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00226.2015. Epub 2015 May 14. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015. PMID: 25977449 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

