Macrophage‑driven pathogenesis in acute lung injury/acute respiratory disease syndrome: Harnessing natural products for therapeutic interventions (Review)
- PMID: 39513609
- PMCID: PMC11551695
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13381
Macrophage‑driven pathogenesis in acute lung injury/acute respiratory disease syndrome: Harnessing natural products for therapeutic interventions (Review)
Abstract
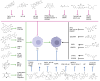
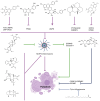
Acute lung injury (ALI) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a common respiratory disease characterized by hypoxemia and respiratory distress. It is associated with high morbidity and mortality. Due to the complex pathogenesis of ALI, the clinical management of patients with ALI/ARDS is challenging, resulting in numerous post‑treatment sequelae and compromising the quality of life of patients. Macrophages, as a class of innate immune cells, play an important role in ALI/ARDS. In recent years, the functions and phenotypes of macrophages have been better understood due to the development of flow cytometry, immunofluorescence, single‑cell sequencing and spatial genomics. However, no macrophage‑targeted drugs for the treatment of ALI/ARDS currently exist in clinical practice. Natural products are important for drug development, and it has been shown that numerous natural compounds from herbal medicine can alleviate ALI/ARDS caused by various factors by modulating macrophage abnormalities. In the present review, the natural products from herbal medicine that can modulate macrophage abnormalities in ALI/ARDS to treat ALI/ARDS are introduced, and their mechanisms of action, discovered in the previous five years (2019‑2024), are presented. This will provide novel ideas and directions for further research, to develop new drugs for the treatment of ALI/ARDS.
Keywords: acute lung injury; acute respiratory distress syndrome; macrophages; natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Natural Compounds Regulate Macrophage Polarization and Alleviate Inflammation Against ALI/ARDS.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 29;15(2):192. doi: 10.3390/biom15020192. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage pyroptosis and its crucial role in ALI/ARDS.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 14;16:1530849. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1530849. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40028334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in preclinical studies of macrophage autophagy in the regulation of ALI/ARDS.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 18;13:922702. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.922702. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36059534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine against acute lung injury: From active ingredients to herbal formulae.Phytomedicine. 2024 Dec;135:155562. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155562. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39536423 Review.
-
Natural product derived phytochemicals in managing acute lung injury by multiple mechanisms.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Jan;163:105224. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105224. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33007416 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, Fan E, Brochard L, Esteban A, Gattinoni L, van Haren F, Larsson A, McAuley DF, et al. Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries. JAMA. 2016;315:788–800. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0291. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

