A case of PLA2R-positive membranous nephropathy with subsequent development of IgG4-related disease
- PMID: 39514162
- PMCID: PMC11958855
- DOI: 10.1007/s13730-024-00941-8
A case of PLA2R-positive membranous nephropathy with subsequent development of IgG4-related disease
Abstract
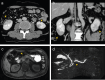
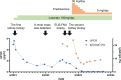
Membranous nephropathy (MN) is a common cause of adult-onset nephrotic syndrome. It is also known as a minor but established renal manifestation of Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD). Previous reports suggest that MN can also be an initial manifestation of IgG4-RD, all of which are phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R)-negative MN. We describe a case of PLA2R-positive MN that subsequently developed other manifestations of IgG4-RD. A 60-year-old male with nephrotic syndrome was diagnosed as primary MN with positive staining for PLA2R on the initial renal biopsy, which remained in partial remission with supportive therapy using angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) without steroid. About 1 year later, a renal mass was detected during an annual checkup, and contrast-enhanced computed tomography revealed low-density masses in bilateral kidneys and the head of the pancreas. The findings of endoscopic biopsy of the pancreatic mass were consistent with autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) and the second renal biopsy showed the findings of MN with tubulointerstitial nephritis, both of which led to a diagnosis of IgG4-RD. The second renal biopsy also showed positive PLA2R. The patient received oral glucocorticoid therapy for IgG4-RD, which improved IgG4-related AIP and renal masses and also resulted in complete remission of MN. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of PLA2R-positive MN with subsequent development of IgG4-RD. It is sometimes difficult to determine whether PLA2R-positive MN occurring with IgG4-RD is primary MN or secondary MN associated with IgG4-RD. The possibility of developing IgG4-RD should be considered even when preceding MN is PLA2R-positive, suggesting of primary MN.
Keywords: Autoimmune pancreatitis; IgG4-related disease; Membranous nephropathy; Nephrotic syndrome; Phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R); Primary membranous nephropathy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: All the authors have declared no competing interest. Ethical approval: All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee at which the studies were conducted (IRB approval number 2879) and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Phospholipase A2 receptor-associated membranous nephropathy in a patient with IgG4-related disease: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 May;98(20):e15616. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015616. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31096469 Free PMC article.
-
Low-density lipoprotein apheresis for PLA2R-related membranous glomerulonephritis accompanied by IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis.CEN Case Rep. 2020 Nov;9(4):395-403. doi: 10.1007/s13730-020-00494-6. Epub 2020 Jun 16. CEN Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32557252 Free PMC article.
-
PLA2R-positive membranous nephropathy in IgG4-related disease.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Feb 23;25(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03511-3. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38395839 Free PMC article.
-
IgG4-related kidney disease (IgG4-RKD) with membranous nephropathy as its initial manifestation: report of one case and literature review.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Jul 16;20(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1419-6. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31311519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary Membranous Nephropathy.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Jun 7;12(6):983-997. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11761116. Epub 2017 May 26. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28550082 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kawano M, Saeki T, Nakashima H, Nishi S, Yamaguchi Y, Hisano S, et al. Proposal for diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011;15(5):615–26. 10.1007/s10157-011-0521-2. - PubMed
-
- Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Lancet. 2015;385(9976):1460–71. 10.1016/s0140-6736(14)60720-0. - PubMed
-
- Cravedi P, Abbate M, Gagliardini E, Galbusera M, Buelli S, Sabadini E, et al. Membranous nephropathy associated with IgG4-related disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011;58(2):272–5. 10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.05.002. - PubMed
-
- Alexander MP, Larsen CP, Gibson IW, Nasr SH, Sethi S, Fidler ME, et al. Membranous glomerulonephritis is a manifestation of IgG4-related disease. Kidney Int. 2013;83(3):455–62. 10.1038/ki.2012.382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

