From defense to disease: IFITM3 in immunity and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39516072
- PMCID: PMC12047391
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurot.2024.e00482
From defense to disease: IFITM3 in immunity and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
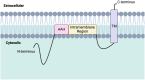
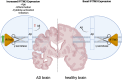
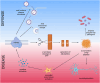
Innate immunity protein interferon induced transmembrane protein 3 (IFITM3) is a transmembrane protein that has a wide array of functions, including in viral infections, Alzheimer's Disease (AD), and cancer. As an interferon stimulated gene (ISG), IFITM3's expression is upregulated by type-I, II, and III interferons. Moreover, the antiviral activity of IFITM3 is modulated by post-translational modifications. IFITM3 functions in innate immunity to disrupt viral fusion and entry to the plasma membrane as well as prevent viral escape from endosomes. As a γ-secretase modulatory protein, IFITM3 distinctly modulates the processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP) to generate amyloid beta peptides (Aβ) and Notch1 cleavages. Increased IFITM3 expression, which can result from aging, cytokine activation, inflammation, and infection, can lead to an upregulation of γ-secretase for Aβ production that causes a risk of AD. Therefore, the prevention of IFITM3 upregulation has potential in the development of novel therapies for the treatment of AD.
Keywords: Amyloid; Infection; Inflammation; Innate immunity; Neuroimmunology; γ-Secretase.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Yue-Ming Li reports a relationship with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center that includes: funding grants. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Periodontitis-induced neuroinflammation triggers IFITM3-Aβ axis to cause alzheimer's disease-like pathology and cognitive decline.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Jul 19;17(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01818-3. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40684176 Free PMC article.
-
Innate Immunity Protein IFITM3 in Alzheimer's Disease.DNA Cell Biol. 2021 Nov;40(11):1351-1355. doi: 10.1089/dna.2021.0585. Epub 2021 Aug 31. DNA Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34468206 Review.
-
The innate immunity protein IFITM3 modulates γ-secretase in Alzheimer's disease.Nature. 2020 Oct;586(7831):735-740. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2681-2. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32879487 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Design of a Portable Birdcage via Meander Line Antenna (MLA) to Lower Beta Amyloid (Aβ) in Alzheimer's Disease.IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2025 Apr 10;13:158-173. doi: 10.1109/JTEHM.2025.3559693. eCollection 2025. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2025. PMID: 40657533 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging approaches to bridging discovery science with clinical care in Alzheimer's disease.Neurotherapeutics. 2025 Apr;22(3):e00589. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2025.e00589. Neurotherapeutics. 2025. PMID: 40246436 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Potential common pathogenesis of several neurodegenerative diseases.Neural Regen Res. 2026 Mar 1;21(3):972-988. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-01054. Epub 2025 May 30. Neural Regen Res. 2026. PMID: 40522761 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease patient brain extracts induce multiple pathologies in novel vascularized neuroimmune organoids for disease modeling and drug discovery.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 May 2. doi: 10.1038/s41380-025-03041-w. Online ahead of print. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40316675
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

