Impact of statistical poly(propylene co-ethylene) on the thermo-mechanical properties of high-density polyethylene
- PMID: 39516232
- PMCID: PMC11549319
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-77467-7
Impact of statistical poly(propylene co-ethylene) on the thermo-mechanical properties of high-density polyethylene
Abstract
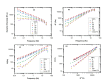
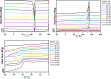
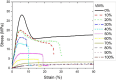
A series of high-density polyethylene and a statistical copolymer of poly(propylene-co-ethylene) blends in a wide range, namely (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60,70, 80, 90, 100) abbreviated as HDPE/VM were systematically investigated by using a rheometer, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) measurements, polarized optical microscopy (POM) and tensile tests. Rheometer results show that adding VM decreases dynamic viscosity, storage, and loss modulus. Han plot shows that HDPE and VM are compatible and miscible in the range from 20 to 60 VM % in the molten state. DSC results show little nucleation effect of VM on HDPE (HDPE's melt crystallization temperature shifts 2 °C higher). Moreover, a linear composition dependence of ∆cp ∆Hc, ∆Hm shows that PE and VM are most probably compatible in the molten state in composition range from 20 to 60%. However, upon crystallization, the VM and PE domains occur distinctively. The results of the tensile tests demonstrated a decrease in elastic modulus, yield stress, and ultimate tensile strength as VM content increased. At low VM content (less than 20%), high elongation at break was detected for the blends, and very fine spherulites of HDPE were found across the sample by POM.
Keywords: DSC; High-density polyethylene; Polarized optical microscopy; Rheological behavior; Statistical poly(propylene-co-ethylene); Stress-strain test.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Crystallinity and Oscillatory Shear Rheology of Polyethylene Blends.Materials (Basel). 2023 Sep 26;16(19):6402. doi: 10.3390/ma16196402. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37834539 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Temperature Mechanical Properties of High-Density and Low-Density Polyethylene and Their Blends.Polymers (Basel). 2021 May 31;13(11):1821. doi: 10.3390/polym13111821. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34072928 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Octene Block Copolymer (OBC) and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) on Crystalline Morphology, Structure and Mechanical Properties of Octene Random Copolymer.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Sep 5;15(18):3655. doi: 10.3390/polym15183655. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765509 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal, creep-recovery and viscoelastic behavior of high density polyethylene/hydroxyapatite nano particles for bone substitutes: effects of gamma radiation.Biomed Eng Online. 2014 Aug 28;13:125. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-13-125. Biomed Eng Online. 2014. PMID: 25168723 Free PMC article.
-
High density polyethylene/graphite nano-composites for total hip joint replacements: processing and in vitro characterization.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011 Oct;4(7):1376-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2011.05.008. Epub 2011 May 11. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011. PMID: 21783148
References
-
- Kar, K. K., Pandey, J. K. & Rana, S. Handbook of polymer nanocomposites. processing, performance and application: volume B: Carbon nanotube based Polymer composites. Handbook of Polymer nanocomposites. Processing, performance and application. Volume B: Carbon Nanotube Based Polym. Compos. 1–601. 10.1007/978-3-642-45229-1 (2015).
-
- FINK, J. K. Handbook of engineering and specialty thermoplastics: Polyolefins and styrenics. Scrivener Publishing vol. 1 Preprint at (2010).
-
- Vasile, C. Handbook of polyolefins. handbook of polyolefins (CRC, 2000). 10.1201/9780203908716
-
- Sae-Oui, P., Sirisinha, C., Sa-nguanthammarong, P. & Thaptong, P. Properties and recyclability of thermoplastic elastomer prepared from natural rubber powder (NRP) and high density polyethylene (HDPE). Polym. Test. 29, (2010).
-
- Polypropylene Handbook. Choice Reviews Online vol. 43. (2006).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

