Overall survival of patients with KIT-mutant metastatic GIST in the era of multiple kinase inhibitor availability
- PMID: 39516299
- PMCID: PMC11549121
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-024-05965-2
Overall survival of patients with KIT-mutant metastatic GIST in the era of multiple kinase inhibitor availability
Erratum in
-
Correction: Overall survival of patients with KIT-mutant metastatic GIST in the era of multiple kinase inhibitor availability.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025 Jan 11;151(1):33. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-06056-y. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39797929 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: The prognosis of patients with metastatic GIST and imatinib-sensitive primary mutations has significantly improved. However, limited data are available to inform patients about outcomes across different lines of treatment. This retrospective analysis aims to evaluate patient outcomes at a large German GIST referral center over the past 15 years.
Patients and methods: Overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were analyzed in patients with metastatic GIST, with diagnosis of metastases between 2008 and 2021, when at least three lines of treatment were available in Germany (n = 174).
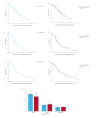
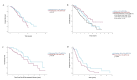
Results: The median overall survival far exceeds historical data for patients with primary exon 11 and exon 9 mutations (median OS in palliative treatment with imatinib: 7.1 years; median OS in second-line palliative treatment with sunitinib: 2.9 years; median OS in third-line palliative treatment with regorafenib: 1.9 years). Among those patients who received palliative imatinib treatment, no significant difference in median OS survival was observed between those who had received perioperative imatinib for localized disease and those who did not. Furthermore, the location of metastases significantly impacted survival, whereas the time between the initial diagnosis and the diagnosis of metastases had no significant effect on survival.
Conclusion: In conclusion, this study provides a novel, real-world reference for survival outcomes in patients with metastatic GIST.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Johanna Falkenhorst: Consulting or Advisory role: Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, DIGIMED Verlag GmbH Sebastian Bauer: Honoraria: Novartis, Pharmamar, GlaxoSmithKline, Deciphera Consulting or Advisory Role: Blueprint Medicines, Bayer, Lilly, Deciphera, Nanobiotix, Daiichi Sankyo, Exelixis, Janssen-Cilag, ADC Therapeutics, Mundipharma, GlaxoSmithKline, Adcendo, Boehringer Ingelheim, IDRX Research Funding: Blueprint Medicines, Novartis, Incyte (Inst) Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Pharmamar.
Figures


References
-
- Bauer S et al (2014) Long-term follow-up of patients with GIST undergoing metastasectomy in the era of imatinib – analysis of prognostic factors (EORTC-STBSG collaborative study). Eur J Surg Oncol (EJSO) 40:412–419 - PubMed
-
- Bauer S, Jones RL, Blay JY, Gelderblom H, George S, Schoffski P, von Mehren M, Zalcberg JR, Kang YK, Razak AA, Trent J, Attia S, Le Cesne A, Su Y, Meade J, Wang T, Sherman ML, Ruiz-Soto R and M. C. Heinrich. 2022. ‘Ripretinib Versus Sunitinib in Patients With Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor After Treatment With Imatinib (INTRIGUE): A Randomized, Open-Label, Phase III Trial’. J Clin Oncol, 40: 3918–3928 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ami E, Barysauskas CM, von Mehren M, Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Butrynski JE, Morgan JA, Wagner AJ, Choy E, Yap JT, Van den Abbeele AD, Solomon SM, Fletcher JA, Demetri GD, George S (2016) Long-term follow-up results of the multicenter phase II trial of regorafenib in patients with metastatic and/or unresectable GI stromal tumor after failure of standard tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Ann Oncol 27:1794–1799 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blanke CD, Demetri GD, Von Mehren M, Heinrich MC, Eisenberg B, Fletcher JA, Corless CL, Fletcher CD, Roberts PJ, Heinz D, Wehre E, Nikolova Z, Joensuu H (2008) Long-term results from a randomized phase II trial of standard- versus higher-dose imatinib mesylate for patients with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors expressing KIT. J Clin Oncol 26:620–625 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

