Biogenic silver nanoparticles incorporated hydrogel beads for anticancer and antibacterial activities
- PMID: 39516320
- PMCID: PMC11549425
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-79003-z
Biogenic silver nanoparticles incorporated hydrogel beads for anticancer and antibacterial activities
Abstract
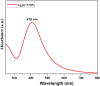
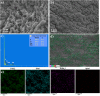
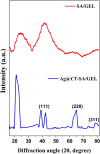
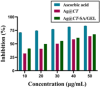
Green nanotechnology is an effective treatment approach being used in cancer research with less adverse effects. This work describes the incorporation of silver nanoparticles synthesized from clitoria ternatea plant extract (Ag@CT NPs) into sodium alginate and gelatin polymer blends (SA/GEL) to produce Ag@CT-SA/GEL polymer beads using calcium chloride (CaCl2) crosslinking agent. Both the formation and the effective incorporation of Ag@CT NPs into polymer blend have been proven by various spectroscopic analysis, surface morphology study and energy dispersive X-ray analysis. Ag@CT NPs and Ag@CT-SA/GEL demonstrate good antibacterial and antioxidant activities comparable to commercially available drug. Dimethyl thiazolyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) anticancer assay and apoptosis study of plant extract and Ag@CT NPs against lung cancer cell lines clearly indicate that Ag@CT-SA/GEL polymer bead can serve as an effective anticancer agent.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Anticancer; Antioxidant; Gelatin; Silver nanoparticle; Sodium alginate.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Bray, F. et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin.68, 394–424 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Das, C. G. A. et al. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles (biosynthesis): A short review on recent advances. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol.27, 101593 (2020).
-
- Kaushal, A. et al. Advances in therapeutic applications of silver nanoparticles. Chem. Biol. Interact.382, 110590 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Sandra, S. et al. Synthesis of electrospun PVA/chitosan nanofibrous scaffold impregnated with CuO nanoparticles for wound healing. Cellulose31, 6387–6401 (2024).
-
- Niveditha, S. et al. Wound healing applications of β-cyclodextrin capped zinc sulphide nanoparticles impregnated electrospun polymeric nanofibrous scaffold. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol.95, 105597 (2024).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

