Identification strategy of wild and cultivated Astragali Radix based on REIMS combined with two-dimensional LC-MS
- PMID: 39516475
- PMCID: PMC11549423
- DOI: 10.1038/s41538-024-00333-3
Identification strategy of wild and cultivated Astragali Radix based on REIMS combined with two-dimensional LC-MS
Abstract
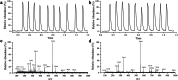
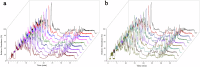
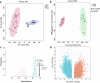
A rapid and real-time method was established based on the combination of rapid evaporative ionization mass spectrometry (REIMS) and two-dimensional liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (2DLC-MS) for identification of wild Astragali Radix (WAR) and cultivated AR (CAR). The samples were analyzed under ambient ionization without time-consuming sample preparation. The phenotypic data of WAR and CAR were used to develop a real-time recognition model. Subsequently, the compounds in these two species were comprehensively characterized based on 2DLC-MS, and 45 different compounds were screened out by multivariate statistical analysis. A semi-quantitative method for 45 different compounds was established based on ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometry (UHPLC-QTRAP-MS). The results showed that the relative content of most compounds in WAR was higher than in CAR. In summary, the method has demonstrated remarkable performance in distinguishing between WAR and CAR, providing a reference in the field of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) analysis and identification.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Discovery of chemical markers for identifying species, growth mode and production area of Astragali Radix by using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry.Phytomedicine. 2020 Feb;67:153155. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153155. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 31901890
-
Rapid quantitative analysis of 12 chemical constituents in wild-simulated and cultivated Astragali Radix based on UHPLC-MS.Chin Herb Med. 2022 Jun 25;14(3):464-469. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2021.06.007. eCollection 2022 Jul. Chin Herb Med. 2022. PMID: 36118005 Free PMC article.
-
Studying the effects of Saposhnikoviae Radix on the pharmacokinetic profiles of 10 bioactive compounds originating from Astragali Radix in rat plasma by UHPLC-QTRAP-MS/MS.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 30;337(Pt 1):118813. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118813. Epub 2024 Sep 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39277063
-
Screening of synthetic PDE-5 inhibitors and their analogues as adulterants: analytical techniques and challenges.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jan;87:176-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.04.037. Epub 2013 May 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 23721687 Review.
-
Insight into chemical basis of traditional Chinese medicine based on the state-of-the-art techniques of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Jun;11(6):1469-1492. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.02.017. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34221863 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fu, J. et al. Review of the botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi). Phytother. Res.28, 1275–1283 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Chen, Z. et al. Astragali Radix (Huangqi): a promising edible immunomodulatory herbal medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol.258, 112895 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Wang, X. et al. Study on genetic diversity of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus populations in inner Mongolia. Chin. J. Grassl.40, 42–48 (2018).
-
- Hu, M. et al. Quality analysis of semi-cultivated Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus from Hunyuan County of Shanxi Province. Chin. Traditional Herb. Drugs43, 1829–1834 (2012).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

