Germline sequencing in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer from the BARCODE2 study reveals a wide range of pathogenic variants in DNA repair genes
- PMID: 39516637
- PMCID: PMC11507020
- DOI: 10.1038/s44276-023-00024-8
Germline sequencing in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer from the BARCODE2 study reveals a wide range of pathogenic variants in DNA repair genes
Abstract
Background: The presence of germline mutations plays an increasingly important role in risk assessment and treatment of prostate cancer (PrCa). Screening for high-risk mutations in subsets of patients is becoming routine. We explore the prevalence of germline genetic mutations in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) recruited to the BARCODE2 trial.
Methods: The BARCODE2 trial is a two-part study investigating the response to carboplatin chemotherapy in mCRPC patients carrying a germline variant in a DNA repair gene (DRG). We report interim data from Part 1, in which participants are recruited for germline genetic testing using a customised next-generation sequencing panel consisting of 115 genes.
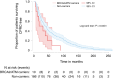
Results: These interim results (N = 220) demonstrate a similar frequency of germline DRG variants in mCRPC patients compared with previously published data (15% detection rate). No significant clinical differences were identified between all carriers and non-carriers, though BRCA2/ATM carriers were found to have a shorter time to mCRPC diagnosis.
Conclusions: Germline pathogenic/likely pathogenic (P/LP) variants in BRCA2 and ATM genes are associated with a shorter time to progression and rarer P/LP variants in other DRG genes may play a role in mCRPC. This justifies the use of routine screening of men with advanced PrCa for germline variants and supports the need for an expanded panel test.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
RE has received honoraria from GU-ASOC, Janssen, University of Chicago, ESMO, Astra Zeneca UK Ltd, DFCI and conducts private practice at RMH, 90S Sloane Street, 280 Kings Road. EH has received honoraria from Accuray Inc, Varian Medical Systems Inc, Astra Zeneca, Janssen-Clag, Bayer, Roche Products Ltd and Merck Sharp & Dohm. KDS has received honoraria (outside of this submitted study) from Sanofi, Astra Zeneca and MSD. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Castro E, Goh C, Leongamornlert D, Saunders E, Tymrakiewicz M, Dadaev T, et al. Effect of BRCA mutations on metastatic relapse and cause-specific survival after radical treatment for localised prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2015;68:186–93. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- ERC-2013-AdG-339208/FP7 Ideas: European Research Council
- ERC-2013-AdG-339208/FP7 Ideas: European Research Council
- ERC-2013-AdG-339208/FP7 Ideas: European Research Council
- ERC-2013-AdG-339208/FP7 Ideas: European Research Council
- ERC-2013-AdG-339208/FP7 Ideas: European Research Council
- ERC-2013-AdG-339208/FP7 Ideas: European Research Council
- ERC-2013-AdG-339208/FP7 Ideas: European Research Council
- ERC-2013-AdG-339208/FP7 Ideas: European Research Council
- NNF20C0059410/Novo Nordisk Foundation Tandem Programme
- NNF20C0059410/Novo Nordisk Foundation Tandem Programme
- NNF20C0059410/Novo Nordisk Foundation Tandem Programme
- NNF20C0059410/Novo Nordisk Foundation Tandem Programme
- NNF20C0059410/Novo Nordisk Foundation Tandem Programme
- NNF20C0059410/Novo Nordisk Foundation Tandem Programme
- NNF20C0059410/Novo Nordisk Foundation Tandem Programme
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous