Real-world effectiveness of CDK 4/6 inhibitors in estrogen-positive metastatic breast cancer
- PMID: 39516670
- PMCID: PMC11523969
- DOI: 10.1038/s44276-024-00070-w
Real-world effectiveness of CDK 4/6 inhibitors in estrogen-positive metastatic breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Initial treatment for advanced ER-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer involves a CDK 4/6 inhibitor (CDK 4/6i). Recent overall survival (OS) analyses led the Danish Medical Council to exclude palbociclib as preferred option. This study aimed to evaluate the real-world effectiveness of abemaciclib, palbociclib, and ribociclib in a Danish context. Additionally, to compare the inhibitors to identify potential endpoint differences.
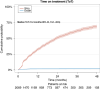
Material and methods: Patients undergoing first or second line CDK 4/6i treatments from January 1st, 2017, until December 31st, 2021 were included. The primary endpoint was progression free survival (PFS).
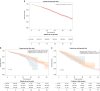
Results: Among 2069 Danish patients, 1554 received first line treatment, 515 received second line treatment. In first line, abemaciclib's median PFS was unreached; palbociclib had a median PFS of 32.0 months (95% CI: 28.9-35.3); ribociclib 42.4 months (95% CI: 35.1-52.9). First-line median OS was 37.8 months (95% CI: 32.5-NA); 49.7 months (95% CI: 44.7-54.1); and 54.4 months (95% CI: 47.9-NA) for abemaciclib, palbociclib and ribociclib, respectively. No significant differences in OS were observed, nor in PFS in second line.
Conclusion: This study confirms first-line CDK 4/6i effectiveness, with abemaciclib and ribociclib showing prolonged PFS vs. palbociclib. This study could not confirm a ranking of the three CDK 4/6i.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MLG: Unrestricted research grant from the Danish Cancer Society. TB: Institutional grants: Pfizer, Astra Zeneca, Novartis, Samsung Bioepis, Seattle Genetics, Merck, Eli Lilly and Danish Cancer Society. Personal grants (advisory board/presentation): Merck, Astra Zeneca, Pfizer and Novartis. Personal grants (travel): Daiichi Sankyo. RG: None. MJ: Meeting expenses and advisory board, Novartis. SN: None. JDR: None. HMN: None. AK: Institutional grants from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Merck, Eli Lilly, Seattle Genetics, Roche, Novartis. Personal grants from Astra Zeneca and Daiichi Sankyo (travel + advisory board), MSD, Novartis, Seagen (Advisory Board). IK: None.
Figures


References
-
- SEER*Explorer Application. 2023. Available from: https://seer.cancer.gov/statistics-network/explorer/application.html?sit....
-
- Deluche E, Antoine A, Bachelot T, Lardy-Cleaud A, Dieras V, Brain E, et al. Contemporary outcomes of metastatic breast cancer among 22,000 women from the multicentre ESME cohort 2008–2016. Eur J Cancer. 2020;129:60–70. 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.01.016. - PubMed
-
- Side 1 af 20 Om Medicinrådet. 2022. Available from: www.medicinraadet.dk.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
