Epidemiology of malignant brain tumors in Genova, Italy. 1993-2017
- PMID: 39516674
- PMCID: PMC11549322
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-79170-z
Epidemiology of malignant brain tumors in Genova, Italy. 1993-2017
Abstract
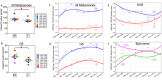
We present an updated analysis on the incidence of primary brain tumors in the Metropolitan Area of Genova, the capital of the northwestern Italian region Liguria.The number of cases and incidence rates for all malignant brain tumors, glioblastoma, malignant brain tumors other than glioblastoma, and brain tumors not otherwise specified were calculated for each of seven three-year and one-eighth four-year periods in which the quarter century 1993-2017 was divided. The rates were age-adjusted (AAR) using the 2013 European standard population, presented per 100,000 person-years and the average percentage change over the three-year period was calculated.The number of cases of all malignant brain tumors and glioblastoma was higher in males than in females in each three-year period and in the entire quarter century 1993-2017. During the latter, the average three-year percentage change in AARs for all brain tumors was minimal [0.6 (95% C.I. = -1.0/2.1) %] while for glioblastoma there was a change of 5.3 (95% C.I. = -0.4/11.3) %. The partially concurrent decline in the incidence rates of malignant brain tumors other than glioblastoma or not otherwise specified suggests that the observed increase in the incidence rate of glioblastoma during 1993-2017 may have been at least partially linked to the improvement during the same period in sensitivity and specificity of the diagnosis of glioblastoma, depleting the reservoirs of other malignant or unspecified brain tumors. Research into possibly increased environmental risk factors (e.g., population exposure to ionizing radiation) for glioblastoma in Genova remains warranted.
Keywords: Age-adjusted rate; Brain cancer; Glioblastoma; Glioma; Incidence; Non-otherwise specified.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Italian cancer figures, report 2012: Cancer in children and adolescents.Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Jan-Feb;37(1 Suppl 1):1-225. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23585445 English, Italian.
-
Italian cancer figures--Report 2015: The burden of rare cancers in Italy.Epidemiol Prev. 2016 Jan-Feb;40(1 Suppl 2):1-120. doi: 10.19191/EP16.1S2.P001.035. Epidemiol Prev. 2016. PMID: 26951748
-
CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2015-2019.Neuro Oncol. 2022 Oct 5;24(Suppl 5):v1-v95. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noac202. Neuro Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36196752 Free PMC article.
-
[SENTIERI - Epidemiological Study of Residents in National Priority Contaminated Sites. Sixth Report].Epidemiol Prev. 2023 Jan-Apr;47(1-2 Suppl 1):1-286. doi: 10.19191/EP23.1-2-S1.003. Epidemiol Prev. 2023. PMID: 36825373 Italian.
-
Triple primary malignant neoplasms including a malignant brain tumor: report of two cases and review of the literature.Surg Neurol. 1996 Mar;45(3):219-29. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(95)00305-3. Surg Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8638217 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of intraoperative flow cytometry on intracranial tumor surgery : a scoping review.Neurosurg Rev. 2025 Sep 9;48(1):637. doi: 10.1007/s10143-025-03789-3. Neurosurg Rev. 2025. PMID: 40924253
-
Understanding Neovascularization in Glioblastoma: Insights from the Current Literature.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 19;26(6):2763. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062763. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141406 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gerstl, J. V. E. et al. A national stratification of the global macroeconomic burden of central nervous system cancer. J. Neurosurg., 1–9 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Vienne-Jumeau, A., Tafani, C. & Ricard, D. Environmental risk factors of primary brain tumors: a review. Rev. Neurol. (Paris). 175, 664–678 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

