Tele-support in breastfeeding: position statement of the Italian society of Neonatology
- PMID: 39516812
- PMCID: PMC11549854
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-024-01816-5
Tele-support in breastfeeding: position statement of the Italian society of Neonatology
Abstract
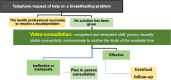
Tele-support in breastfeeding can be defined as any support provided by a service that connects health workers and/or lactation consultants with breastfeeding parents through video visits, although a telephone contact with the breastfeeding mother remains the first method of remote breastfeeding support. The tele-support in breastfeeding has increased significantly during the SARS-CoV2 pandemic worldwide and, given its effectiveness, may be maintained also after the pandemic. The Italian Society of Neonatology on the basis of: 1) two focus group studies on the tele-support in breastfeeding conducted in Italy with 11 Neonatal Intensive Care Unit nurses and 10 neonatologists, respectively, 2) a national survey on tele-support in breastfeeding addressing the Italian Neonatal Intensive Care Units, and 3) a review of the available experiences and literature, has provided a Position Statement, limitedly to the individual tele-support in breastfeeding. The Italian Society of Neonatology states that: 1) the tele-support in breastfeeding can be used when a consultation in person is not shortly available and may allow to select those situations that require an in-person visit; 2) the organization of a tele-support in breastfeeding session requires the use of a competent, dedicated healthcare staff (specifically trained and/or with adequate experience) and an appropriate methodology while preparing, running and concluding the support session. According to Italian Society of Neonatology the tele-support in breastfeeding may be an effective intervention to promote breastfeeding as a complementary method to the in-person assistance and should be possibly provided in an integrated manner by the Community Health Services and the Maternity Hospital.
Keywords: Breastfeeding; Focus group; Maternity Hospitals; Position statement; Survey; Tele-support.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All Authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Bird K. Telemedicine; concept and practice. Springfield, Illinois: Thomas; 1975.
-
- WHO Group Consultation on Health Telematics. A health telematics policy in support of WHO’s health-for-all strategy for global health development: report of the WHO Group consultation on health telematics. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 1997. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/63857 Accessed on 19 July 2024.
-
- Ferraz Dos Santos L, Borges RF, de Azambuja DA. Telehealth and Breastfeeding: an Integrative Review. Telemedicne and e-Health 2020;26(7):837–846. 10.1089/tmj.2019.0073. Epub 2019 Oct 18. PMID: 31633467. - PubMed