Effects of Hyrax Maxillary Expander on Nasal Cavity and Upper Airway in Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39517360
- PMCID: PMC11544907
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare12212148
Effects of Hyrax Maxillary Expander on Nasal Cavity and Upper Airway in Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Whether Hyrax maxillary expander is an effective treatment for maxillary transverse deficiency as well as expansion of the upper airway is still controversial. The study's purpose was to evaluate 3D changes in upper airway dimensions of adolescent patients measured primarily by cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) after rapid maxillary expansion (RME) with the Hyrax maxillary expander.
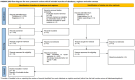
Methods: Studies up to 1 April 2024 were searched in the following databases: PubMed/MEDICINE, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Embase. Inclusion criteria were clinical trials and cohort studies that assessed the effect of RME in adolescent patients with upper airway stenosis using CBCT-based three-dimensional analysis. The risk of bias in the study outcomes was assessed using the Cochrane Collaboration's risk of bias tool, the GRADE method, and a tool for evaluating non-randomized controlled study (non-RCT) literature from a previous systematic review, depending on the types of articles. The study was reported in accordance with PRISMA guidelines.
Results: The study conducted a random effects meta-analysis of mean differences and 95% confidence intervals for changes in upper airway volumes, including the nasal cavity (NC), in the outcomes of 16 included studies, followed by subgroup analyses.
Conclusion: A significant increase in nasopharynx volume was observed after rapid maxillary expansion (RME) by Hyrax maxillary expander (MD = 0.69, 95% CI (0.09~1.28), p = 0.02).
Keywords: hyrax expander; nasal cavity; rapid maxillary expansion; upper airway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


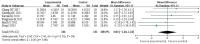

Similar articles
-
Three-dimensional analyses of short- and long-term effects of rapid maxillary expansion on nasal cavity and upper airway: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Orthod Craniofac Res. 2020 Aug;23(3):250-276. doi: 10.1111/ocr.12378. Epub 2020 May 5. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2020. PMID: 32248642
-
The upper airway volume effects produced by Hyrax, Hybrid-Hyrax, and Keles keyless expanders: a single-centre randomized controlled trial.Eur J Orthod. 2021 Jun 8;43(3):254-264. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjaa031. Eur J Orthod. 2021. PMID: 32377675 Clinical Trial.
-
Interest of miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion on the upper airway in growing patients: A systematic review.Int Orthod. 2022 Sep;20(3):100657. doi: 10.1016/j.ortho.2022.100657. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Int Orthod. 2022. PMID: 35752557
-
Three-dimensional evaluation of upper airway following rapid maxillary expansion: a CBCT study.Angle Orthod. 2014 Mar;84(2):265-73. doi: 10.2319/012313-71.1. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Angle Orthod. 2014. PMID: 23865825 Free PMC article.
-
Dento-skeletal effects produced by rapid versus slow maxillary expansion using fixed jackscrew expanders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Orthod. 2021 Jun 8;43(3):301-312. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjaa086. Eur J Orthod. 2021. PMID: 33950178
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

