Novel Applications in Controlled Drug Delivery Systems by Integrating Osmotic Pumps and Magnetic Nanoparticles
- PMID: 39517939
- PMCID: PMC11548579
- DOI: 10.3390/s24217042
Novel Applications in Controlled Drug Delivery Systems by Integrating Osmotic Pumps and Magnetic Nanoparticles
Abstract
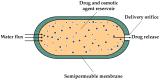
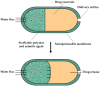
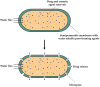
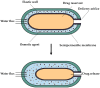
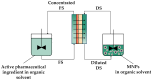
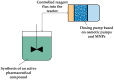
The alarming rise in chronic diseases worldwide highlights the urgent need to overcome the limitations of conventional drug delivery systems. In this context, osmotic pumps are able to release drugs by differential osmotic pressure, achieving a controlled rate independent of physiological factors and reducing the dosing frequency. As osmotic pumps are based on the phenomenon of osmosis, the choice of high osmolality draw solutions (DSs) is a critical factor in the successful delivery of the target drug. Therefore, one alternative that has received particular attention is the formulation of DSs with magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) due to their easy recovery, negligible reverse solute flux (RSF), and their possible tailor-made functionalization to generate high osmotic gradients. In this work, the possible integration of DSs formulated with MNPs in controlled drug delivery systems is discussed for the first time. In particular, the main potential advantages that these novel medical devices could offer, including improved scalability, regeneration, reliability, and enhanced drug delivery performance, are provided and discussed. Thus, the results of this review may demonstrate the potential of MNPs as osmotic agents, which could be useful for advancing the design of osmotic pump-based drug delivery systems.
Keywords: draw solutions; drug delivery; forward osmosis; magnetic nanoparticles; medical devices; osmotic pressure; osmotic pumps.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Succinate Functionalization of Hyperbranched Polyglycerol-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Draw Solute During Forward Osmosis.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015 Oct;15(10):8279-84. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2015.11244. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26726503
-
Recent Aspects of Osmotic Pump Systems: Functionalization, Clinical use and Advanced Imaging Technology.Curr Drug Metab. 2016;17(3):279-91. doi: 10.2174/1389200216666151015115706. Curr Drug Metab. 2016. PMID: 26467064 Review.
-
Desalination of brackish water by gelatin-coated magnetite nanoparticles as a novel draw solute in forward osmosis process.Environ Technol. 2021 Jul;42(18):2885-2895. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2020.1717642. Epub 2020 Jan 29. Environ Technol. 2021. PMID: 31950874
-
Synthesis of Poly-Sodium-Acrylate (PSA)-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Use in Forward Osmosis Draw Solutions.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019 Aug 31;9(9):1238. doi: 10.3390/nano9091238. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31480419 Free PMC article.
-
Osmotic Pump Drug Delivery Systems-A Comprehensive Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Nov 18;15(11):1430. doi: 10.3390/ph15111430. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36422560 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization Noncommunicable Diseases. [(accessed on 24 January 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases.
-
- World Health Organization . Access to NCD Medicines: Emergent Issues during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Key Structural Factors. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2023.
-
- United Nations Chronic Diseases Taking ‘Immense and Increasing Toll on Lives’, Warns WHO. [(accessed on 24 January 2024)]. Available online: https://news.un.org/en/story/2023/05/1136832.
-
- United Nations Access to Chronic Disease Medication ‘Still out of Reach for Many’: WHO Report. [(accessed on 24 January 2024)]. Available online: https://news.un.org/en/story/2023/03/1134902.
-
- The Global Goals Good Health and Well-Being. [(accessed on 24 January 2024)]. Available online: https://www.globalgoals.org/goals/3-good-health-and-well-being/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PID2020-115409RB-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades; Agencia Estatal de Investigación
- PDC2021-673 120786-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades; Agencia Estatal de Investigación; European Union Next Generation EU/PRTR
- TED2021-129874B-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades; Agencia Estatal de Investigación; European Union Next Generation EU/PRTR
- Concepción Arenal predoctoral contract UC-23-28/University of Cantabria
- PRE2019-089339/Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities; Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades; Agencia Estatal de Investigación; ESF Investing in your future
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

