Bio-Based and Biodegradable Polymeric Materials for a Circular Economy
- PMID: 39518225
- PMCID: PMC11548373
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16213015
Bio-Based and Biodegradable Polymeric Materials for a Circular Economy
Abstract
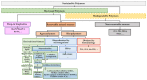
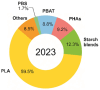
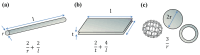
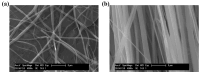
Nowadays, plastic contamination worldwide is a concerning reality that can be addressed with appropriate society education as well as looking for innovative polymeric alternatives based on the reuse of waste and recycling with a circular economy point of view, thus taking into consideration that a future world without plastic is quite impossible to conceive. In this regard, in this review, we focus on sustainable polymeric materials, biodegradable and bio-based polymers, additives, and micro/nanoparticles to be used to obtain new environmentally friendly polymeric-based materials. Although biodegradable polymers possess poorer overall properties than traditional ones, they have gained a huge interest in many industrial sectors due to their inherent biodegradability in natural environments. Therefore, several strategies have been proposed to improve their properties and extend their industrial applications. Blending strategies, as well as the development of composites and nanocomposites, have shown promising perspectives for improving their performances, emphasizing biopolymeric blend formulations and bio-based micro and nanoparticles to produce fully sustainable polymeric-based materials. The Review also summarizes recent developments in polymeric blends, composites, and nanocomposite plasticization, with a particular focus on naturally derived plasticizers and their chemical modifications to increase their compatibility with the polymeric matrices. The current state of the art of the most important bio-based and biodegradable polymers is also reviewed, mainly focusing on their synthesis and processing methods scalable to the industrial sector, such as melt and solution blending approaches like melt-extrusion, injection molding, film forming as well as solution electrospinning, among others, without neglecting their degradation processes.
Keywords: bio-based polymers; biodegradable polymers; circular economy; degradation; nanocomposites; nanoparticles; natural polymers; plasticizers; processing; revalorization; sustainable polymers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

























References
-
- Bachmann M., Zibunas C., Hartmann J., Tulus V., Suh S., Guillén-Gosálbez G., Bardow A. Towards Circular Plastics within Planetary Boundaries. Nat. Sustain. 2023;6:599–610. doi: 10.1038/s41893-022-01054-9. - DOI
-
- Nagel B., Dellweg H., Gierasch L.M. Glossary for Chemists of Terms Used in Biotechnology (IUPAC Recommendations 1992) Pure Appl. Chem. 1992;64:143–168. doi: 10.1351/pac199264010143. - DOI
-
- Vert M., Doi Y., Hellwich K.-H., Hess M., Hodge P., Kubisa P., Rinaudo M., Schué F. Terminology for Biorelated Polymers and Applications (IUPAC Recommendations 2012) Pure Appl. Chem. 2012;84:377–410. doi: 10.1351/PAC-REC-10-12-04. - DOI
-
- Biswas M.C., Jony B., Nandy P.K., Chowdhury R.A., Halder S., Kumar D., Ramakrishna S., Hassan M., Ahsan M.A., Hoque M.E., et al. Recent Advancement of Biopolymers and Their Potential Biomedical Applications. J. Polym. Environ. 2022;30:51–74. doi: 10.1007/s10924-021-02199-y. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

