The Effects of an 8-Month Multicomponent Training Program in Body Composition, Functional Fitness, and Sleep Quality in Aged People: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 39518745
- PMCID: PMC11546580
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13216603
The Effects of an 8-Month Multicomponent Training Program in Body Composition, Functional Fitness, and Sleep Quality in Aged People: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
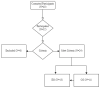
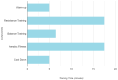
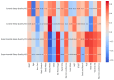
Background/Objectives: This study examined the effects of an intervention on anthropometrics, body composition, physical fitness, and sleep quality in aged individuals, comparing a control group (N = 11) and an experimental group (N = 13) across two measurement points. Methods: A multicomponent training program of 8 months was adopted as the intervention group. A bioimpedance balance, functional fitness test, and Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index measured body composition, functional fitness, and sleep quality. Results: Both groups showed minimal changes in body mass and hand grip strength. However, the experimental group experienced significant improvements in physical fitness, including a 26% increase in arm curl repetitions, an 18% reduction in 5 times sit-to-stand (5TSTS) completion time, and a 29% rise in 2-min step test (2MST) steps, indicating enhanced muscle endurance and cardiovascular fitness. Flexibility decreased significantly in the experimental group, while body fat percentage was reduced by 10%. Sleep quality improved by 47% in the experimental group but declined by 14% in the control group. Correlational analysis revealed that better sleep quality was linked to improved fitness performance and reduced body fat in the experimental group, with post-intervention results further confirming the connection between sleep and fat reduction. In the control group, improved sleep quality was associated with higher metabolic rates after 8 months. Conclusions: These findings suggest that the intervention positively impacted physical fitness and sleep quality, with potential benefits for overall health.
Keywords: ageing; fitness; quality; sleep.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does nutritional status influence the effects of a multicomponent exercise programme on body composition and physical fitness in older adults with limited physical function?Eur J Sport Sci. 2023 Jul;23(7):1375-1384. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2022.2092426. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Eur J Sport Sci. 2023. PMID: 35816744 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of a machine-assisted healthy physical fitness promotion program for community elderly.J Chin Med Assoc. 2020 Aug;83(8):779-783. doi: 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000308. J Chin Med Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32217983
-
Performance on sit-to-stand tests in relation to measures of functional fitness and sarcopenia diagnosis in community-dwelling older adults.Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2021 Jan 8;18(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s11556-020-00255-5. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2021. PMID: 33419399 Free PMC article.
-
The preliminary effect of whole-body vibration intervention on improving the skeletal muscle mass index, physical fitness, and quality of life among older people with sarcopenia.BMC Geriatr. 2018 Jan 17;18(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12877-018-0712-8. BMC Geriatr. 2018. PMID: 29343219 Free PMC article.
-
Combined training prescriptions for improving cardiorespiratory fitness, physical fitness, body composition, and cardiometabolic risk factors in older adults: Systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled trials.Sci Sports. 2023 Feb 17. doi: 10.1016/j.scispo.2022.03.015. Online ahead of print. Sci Sports. 2023. PMID: 36843900 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Science of Shape: How Physical Activity, Sleep, and Stress Affect Body Composition.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Apr 20;13(8):949. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13080949. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40281898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Exercise on Balance Function in People with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Jun 1;13(11):1312. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13111312. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Multicomponent Training on Clinical, Functional, and Psychological Outcomes in Cardiovascular Disease: A Narrative Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Apr 29;61(5):822. doi: 10.3390/medicina61050822. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40428780 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Martellucci S., Pagliuca G., de Vincentiis M., Greco A., De Virgilio A., Nobili Benedetti F.M., Gallipoli C., Rosato C., Clemenzi V., Gallo A. Features of Residual Dizziness after Canalith Repositioning Procedures for Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2016;154:693–701. doi: 10.1177/0194599815627624. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhou L., Gong W., Wang S., Guo Z., Liu M., Chuang S., Bao D., Zhou J. Combined Balance and Plyometric Training Enhances Knee Function, but Not Proprioception of Elite Male Badminton Players: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Study. Front. Psychol. 2022;13:947877. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.947877. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Soares N.M.M., Dantas E.H.M., da Silva-Grigoletto M.E., dos Santos Silva R.J., Aidar F.J.M., da Silva Júnior W.M., Cabral B.T., Carneiro A.L., Garrido N.D., Reis V.M. CIAFIS—Congresso Internacional de Atividade Física, Nutrição e Saúde. Motricidade. 2018;13:1–200. doi: 10.6063/motricidade.14077. - DOI
-
- Suzuki T., Shimada H., Makizako H., Doi T., Yoshida D., Tsutsumimoto K., Anan Y., Uemura K., Lee S., Park H. Effects of Multicomponent Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults with Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Neurol. 2012;12:128. doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-12-128. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources