High Behavioral Reactivity to Novelty as a Susceptibility Factor for Memory and Anxiety Disorders in Streptozotocin-Induced Neuroinflammation as a Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 39519114
- PMCID: PMC11546707
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252111562
High Behavioral Reactivity to Novelty as a Susceptibility Factor for Memory and Anxiety Disorders in Streptozotocin-Induced Neuroinflammation as a Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
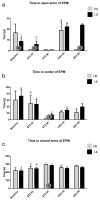
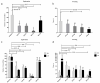
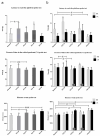
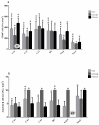
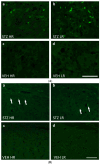
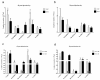
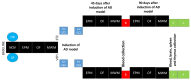
Individual differences in responsiveness to environmental factors, including stress reactivity and anxiety levels, which differ between high (HR) and low (LR) responders to novelty, might be risk factors for development of memory and anxiety disorders in sporadic Alzheimer's disease (sAD). In the present study, we investigated whether behavioral characteristics of the HR and LR rats, influence the progression of sAD (neuroinflammation, β-amyloid peptide, behavioral activity related to memory (Morris water maze) and anxiety (elevated plus maze, white and illuminated open field test) in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced neuroinflammation as a model of early pathophysiological alterations in sAD. Early (45 days) in disease progression, there was a more severe impairment of reference memory and higher levels of anxiety in HRs compared with LRs. Behavioral depression in HRs was associated with higher expression of β-amyloid deposits, particularly in the NAcS, and activation of microglia (CD68+ cells) in the hypothalamus, as opposed to less inflammation in the hippocampus, particularly in CA1, compared with LRs in late (90 days) sAD progression. Our findings suggest that rats with higher behavioral activity and increased responsivity to stressors show more rapid progression of disease and anxiety disorders compared with low responders to novelty in the STZ-induced sAD model.
Keywords: Morris water maze; cytokines; elevated plus maze; high and low responders to novelty; neuroinflammation; rat Alzheimer’s disease model; spatial memory and anxiety disorders; streptozotocin; white and illuminated open field; β-amyloid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decrease in Adult Neurogenesis and Neuroinflammation Are Involved in Spatial Memory Impairment in the Streptozotocin-Induced Model of Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease in Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 May;55(5):4280-4296. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0645-9. Epub 2017 Jun 16. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28623617
-
Andrographolide Attenuates Short-Term Spatial and Recognition Memory Impairment and Neuroinflammation Induced by a Streptozotocin Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Neurotox Res. 2022 Oct;40(5):1440-1454. doi: 10.1007/s12640-022-00569-5. Epub 2022 Aug 27. Neurotox Res. 2022. PMID: 36029454
-
Neuroprotection elicited by taurine in sporadic Alzheimer-like disease: benefits on memory and control of neuroinflammation in the hippocampus of rats.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Oct;479(10):2663-2678. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04872-3. Epub 2023 Oct 24. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37874493
-
Neurotrophic factor neuritin ameliorates streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer's disease-like impairment of memory, neuroinflammation, apoptotic factors and compensates hippocampal neuritin expression.Behav Brain Res. 2025 May 28;486:115542. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2025.115542. Epub 2025 Mar 22. Behav Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 40127821
-
siRNA Mediated GSK3β Knockdown Targets Insulin Signaling Pathway and Rescues Alzheimer's Disease Pathology: Evidence from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022 Jan 12;14(1):69-93. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c15305. Epub 2021 Dec 30. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022. PMID: 34967205
Cited by
-
Central Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Treatment Enhances Working and Reference Memory by Reducing Neuroinflammation and Amyloid Beta Deposition in a Rat Model of Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Apr 4;18(4):527. doi: 10.3390/ph18040527. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283962 Free PMC article.
-
Central Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1-Induced Anxiolytic and Antidepressant Effects in a Rat Model of Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease Are Associated with the Peripheral Suppression of Inflammation.Cells. 2025 Aug 1;14(15):1189. doi: 10.3390/cells14151189. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40801621 Free PMC article.
-
Galactooligosaccharides Attenuate Behavioural, Haematological and Immunological Abnormalities and Influence Gut Microbiota in Rats with Amygdala Hyperactivation Induced by Electrical Stimulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 3;26(9):4353. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094353. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362590 Free PMC article.
-
Species-specific sensitivity to intracerebroventricular streptozotocin in rats and mice highlights pathways and proteins relevant to Alzheimer's disease.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2025 Jun 1. doi: 10.1007/s00702-025-02952-w. Online ahead of print. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2025. PMID: 40450637
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

