Phenotypic Biomarkers of Aqueous Extracellular Vesicles from Retinoblastoma Eyes
- PMID: 39519212
- PMCID: PMC11545953
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252111660
Phenotypic Biomarkers of Aqueous Extracellular Vesicles from Retinoblastoma Eyes
Abstract
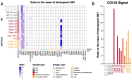
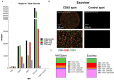
Recent advancements in aqueous humor (AH) cell-free DNA (cfDNA) genomics have opened new avenues for ex vivo molecular profiling of retinoblastoma (RB), the most common pediatric intraocular malignancy, where biopsy is typically prohibited. While these insights offer a genetic blueprint of the tumor, they lack multi-omic molecular phenotyping, which is essential for understanding the functional state. Extracellular vesicles (EVs), naturally present in AH, are promising by offering time-resolved phenotypic information. We employed multiplex bead-based flow cytometry and Single Extracellular Vesicle Nanoscopy (SEVEN) to analyze EV phenotypes in AH from a cohort of five RB, with three uveal melanoma (UM) and two age-matched glaucoma (GLC) samples serving as controls. The studies identified CD133-enriched EVs uniquely in RB AH, absent in both GLC and UM AH. This was corroborated by further analysis of five RB cell lines, including two commercial (Y79, Weri) and three in-house developed lines, confirming CD133 enrichment and supporting its role as an RB-specific EV marker. Single-vesicle analysis demonstrated a strong association of CD133 with CD81 and CD63, with minimal CD9 presence. These results, validated through complementary techniques, position CD133 as a critical marker in RB-derived EVs, paving the way for enhanced multi-omic RB characterization and potential advancements in clinical diagnostics.
Keywords: CD133; aqueous humor; extracellular vesicles; molecular phenotyping; retinoblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Jesse Lee Berry and Liya Xu have filed a patent, “Aqueous Humor Cell-Free DNA for Diagnostic and Prognostic Evaluation of Ophthalmic Disease”. Part of the methodology used in this work is the subject of a provisional patent application. Tijana Jovanovic-Talisman may be entitled to certain compensation through their institutions’ respective intellectual property policies in the event such intellectual property is licensed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Diverse Populations of Extracellular Vesicles with Opposite Functions during Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection.J Virol. 2021 Feb 24;95(6):e02357-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02357-20. Print 2021 Feb 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33361424 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell somatic copy number alteration profiling of vitreous humor seeds in retinoblastoma.Ophthalmic Genet. 2024 Dec;45(6):646-649. doi: 10.1080/13816810.2024.2374886. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Ophthalmic Genet. 2024. PMID: 39016001
-
ALYREF/THOC4 expression and cell growth modulation in retinoblastoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Aug;260:155392. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155392. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38880039
-
Malignant Transformation of Ocular Melanocytoma to Uveal Melanoma: A Clinicopathologic Review of Three Novel Unsuspected Cases of a Likely Under-Recognized Phenomenon, With Review of the Literature and Molecular Genetic Data.Am J Ophthalmol. 2025 Aug;276:126-145. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2025.03.044. Epub 2025 Mar 31. Am J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40174716 Review.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roy S.R., Kaliki S. Retinoblastoma: A Major Review. Mymensingh Med. J. 2021;30:881–895. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

