GdVO4:Eu3+ and LaVO4:Eu3+ Nanoparticles Exacerbate Oxidative Stress in L929 Cells: Potential Implications for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 39519237
- PMCID: PMC11546343
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252111687
GdVO4:Eu3+ and LaVO4:Eu3+ Nanoparticles Exacerbate Oxidative Stress in L929 Cells: Potential Implications for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
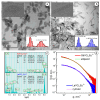
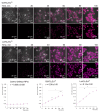
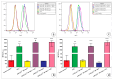
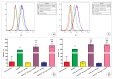
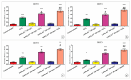
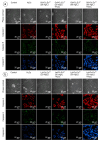
The therapeutic potential of redox-active nanoscale materials as antioxidant- or reactive oxygen species (ROS)-inducing agents was intensely studied. Herein, we demonstrate that the synthesized and characterized GdVO4:Eu3+ and LaVO4:Eu3+ nanoparticles, which have been already shown to have redox-active, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and wound healing properties, both in vitro and in vivo, worsen oxidative stress of L929 cells triggered by hydrogen peroxide or tert-butyl hydroperoxide (tBuOOH) at the concentrations that are safe for intact L929 cells. This effect was observed upon internalization of the investigated nanosized materials and is associated with the cleavage of caspase-3 and caspase-9 without recruitment of caspase-8. Such changes in the caspase cascade indicate activation of the intrinsic caspase-9-dependent mitochondrial but not the extrinsic death, receptor-mediated, and caspase-8-dependent apoptotic pathway. The GdVO4:Eu3+ and LaVO4:Eu3+ nanoparticle-induced apoptosis of oxidatively compromised L929 cells is mediated by ROS overgeneration, Ca2+ overload, endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase), and DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 (DDIT3). Our findings demonstrate that GdVO4:Eu3+ and LaVO4:Eu3+ nanoparticles aggravate the oxidative stress-induced damage to L929 cells, indicating that they might potentially be applied as anti-cancer agents.
Keywords: apoptosis; caspase; intrinsic apoptosis; nanoparticles; nanotoxicity; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Rare-earth orthovanadate nanoparticles trigger Ca2+-dependent eryptosis.Nanotechnology. 2023 Mar 1;34(20). doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/acbb7f. Nanotechnology. 2023. PMID: 36780664
-
Silica nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage is followed by activation of intrinsic apoptosis pathway in glioblastoma cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Apr 12;13:2279-2294. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S158393. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29695906 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effect of cerium nanoparticles on the viability, redox-status and Ca2+-signaling system of cancer cells of various origins.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2025 Feb;764:110261. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2024.110261. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39645139
-
l-Serine protects mouse hippocampal neuronal HT22 cells against oxidative stress-mediated mitochondrial damage and apoptotic cell death.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Sep;141:447-460. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.07.018. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31326607
-
Suppression of Apoptosis in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs) by Klotho Protein is Associated with Reduced Endoplasmic Reticulum Oxidative Stress and Activation of the PI3K/AKT Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Nov 24;24:8489-8499. doi: 10.12659/MSM.911202. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30471224 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

