Kinin Receptors B1 and B2 Mediate Breast Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion by Activating the FAK-Src Axis
- PMID: 39519260
- PMCID: PMC11546324
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252111709
Kinin Receptors B1 and B2 Mediate Breast Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion by Activating the FAK-Src Axis
Abstract
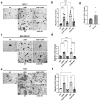
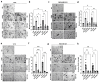
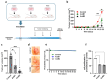
Kinin receptors B1 and B2 are involved in migration and invasion in gastric, glioma, and cervical cancer cells, among others. However, the role of kinin receptors in breast cancer cells has been poorly studied. We aimed to reveal the impact of B1 and B2 receptors on migration and invasion in breast cancer cells and demonstrate their capacity to modulate in vivo tumor growth. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, and T47D cells treated with Lys-des[Arg9]bradykinin (LDBK) or bradykinin (BK) were used to evaluate migration and invasion. Des-[Arg9]-Leu8-BK and HOE-140 were used as antagonists for the B1 and B2 receptors. MDA-MB-231 cells incubated or not with antagonists were subcutaneously inoculated in BALBc NOD/SCID mice to evaluate tumor growth. LDBK and BK treatment significantly increased migration and invasion in breast cancer cells, effects that were negated when antagonists were used. The use of antagonists in vivo inhibited tumor growth. Moreover, the migration and invasion induced by kinins in breast cancer cells were inhibited when focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and Src inhibitors were used. The novelty revealed in our work is that B1 and B2 receptors activated by LDBK and BK induce migration and invasion in breast cancer cells via a mechanism that involves the FAK-Src signaling pathway, and the antagonism of both receptors in vivo impairs breast tumor growth.
Keywords: B1 receptor; B2 receptor; FAK; Src; breast cancer; invasion; kinin receptors; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Functional and molecular characterization of kinin B1 and B 2 receptors in human bladder cancer: implication of the PI3Kγ pathway.Invest New Drugs. 2013 Aug;31(4):812-22. doi: 10.1007/s10637-012-9907-6. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Invest New Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23224295
-
Characterization of bradykinin receptors in a human osteoblastic cell line.Regul Pept. 2002 Jan 15;103(1):39-51. doi: 10.1016/s0167-0115(01)00325-1. Regul Pept. 2002. PMID: 11738247
-
Mechanisms involved in kinin-induced glioma cells proliferation: the role of ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt pathways.J Neurooncol. 2014 Nov;120(2):235-44. doi: 10.1007/s11060-014-1549-4. Epub 2014 Jul 24. J Neurooncol. 2014. PMID: 25056222
-
International union of pharmacology. XLV. Classification of the kinin receptor family: from molecular mechanisms to pathophysiological consequences.Pharmacol Rev. 2005 Mar;57(1):27-77. doi: 10.1124/pr.57.1.2. Pharmacol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15734727 Review.
-
Bifunctional ligands of the bradykinin B2 and B1 receptors: An exercise in peptide hormone plasticity.Peptides. 2018 Jul;105:37-50. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2018.05.007. Epub 2018 May 23. Peptides. 2018. PMID: 29802875 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

