T Regulatory Cell Subsets Do Not Restore for One Year After Acute COVID-19
- PMID: 39519310
- PMCID: PMC11545974
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252111759
T Regulatory Cell Subsets Do Not Restore for One Year After Acute COVID-19
Abstract
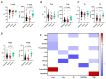
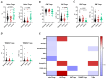
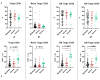
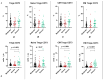
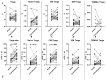
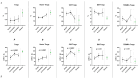
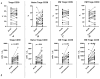
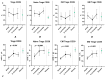
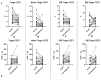
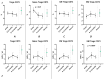
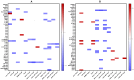
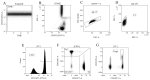
COVID-19, caused by SARS-CoV-2, triggers a complex immune response, with T regulatory cells (Tregs) playing a crucial role in maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing excessive inflammation. The current study investigates the function of T regulatory cells during COVID-19 infection and the subsequent recovery period, emphasizing their impact on immune regulation and inflammation control. We conducted a comprehensive analysis of Treg subpopulations in peripheral blood samples from COVID-19 patients at different stages: acute infection, early convalescence, and long-term recovery. Flow cytometry was employed to quantify Tregs including "naïve", central memory (CM), effector memory (EM), and terminally differentiated CD45RA+ effector cells (TEMRA). Additionally, the functional state of the Tregs was assessed by the expression of purinergic signaling molecules (CD39, CD73). Cytokine profiles were assessed through multiplex analysis. Our findings indicate a significant decrease in the number of Tregs during the acute phase of COVID-19, which correlates with heightened inflammatory markers and increased disease severity. Specifically, we found a decrease in the relative numbers of "naïve" and an increase in EM Tregs, as well as a decrease in the absolute numbers of "naïve" and CM Tregs. During the early convalescent period, the absolute counts of all Treg populations tended to increase, accompanied by a reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines. Despite this, one year after recovery, the decreased subpopulations of regulatory T cells had not yet reached the levels observed in healthy donors. Finally, we observed the re-establishment of CD39 expression in all Treg subsets; however, there was no change in CD73 expression among Tregs. Understanding these immunological changes across different T regulatory subsets and adenosine signaling pathways offers important insights into the disease's pathogenesis and provides a broader view of immune system dynamics during recovery.
Keywords: COVID-19; T regulatory cells; convalescent period; multicolor flow cytometry; purinergic signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phenotypical analysis of ectoenzymes CD39/CD73 and adenosine receptor 2A in CD4+ CD25high Foxp3+ regulatory T-cells in psoriasis.Australas J Dermatol. 2018 Feb;59(1):e31-e38. doi: 10.1111/ajd.12561. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Australas J Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 28295154 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the CD39/CD73 Axis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The CD73- Phenotype Identifies Polyfunctional Cytotoxic Lymphocytes.Cells. 2020 Jul 22;9(8):1750. doi: 10.3390/cells9081750. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32707842 Free PMC article.
-
CD39/CD73 and the imbalance of Th17 cells and regulatory T cells in allergic asthma.Mol Med Rep. 2013 Nov;8(5):1432-8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1692. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Mol Med Rep. 2013. PMID: 24065069
-
Targeting adenosine and regulatory T cells in cancer immunotherapy.Hum Immunol. 2021 Apr;82(4):270-278. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2020.12.005. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Hum Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33610376 Review.
-
CD73 and CD39 ectonucleotidases in T cell differentiation: Beyond immunosuppression.FEBS Lett. 2015 Nov 14;589(22):3454-60. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.07.027. Epub 2015 Jul 29. FEBS Lett. 2015. PMID: 26226423 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

