Magnetic MgFeO@BC Derived from Rice Husk as Peroxymonosulfate Activator for Sulfamethoxazole Degradation: Performance and Reaction Mechanism
- PMID: 39519319
- PMCID: PMC11546872
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252111768
Magnetic MgFeO@BC Derived from Rice Husk as Peroxymonosulfate Activator for Sulfamethoxazole Degradation: Performance and Reaction Mechanism
Abstract
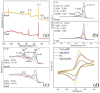
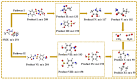
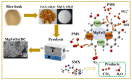
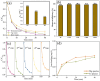
Heterogeneous Mg-Fe oxide/biochar (MgFeO@BC) nanocomposites were synthesized by a co-precipitation method and used as biochar-based catalysts to activate peroxymonosulfate (PMS) for sulfamethoxazole (SMX) removal. The optimal conditions for SMX degradation were examined as follows: pH 7.0, MgFeO@BC of 0.4 g/L, PMS concentration of 0.6 mM and SMX concentration of 10.0 mg/L at 25 ℃. In the MgFeO@BC/PMS system, the removal efficiency of SMX was 99.0% in water within 40 min under optimal conditions. In the MgFeO@BC/PMS system, the removal efficiencies of tetracycline (TC), cephalexin (CEX), ciprofloxacin (CIP), 4-chloro-3-methyl phenol (CMP) and SMX within 40 min are 95.3%, 98.4%, 98.2%, 97.5% and 99.0%, respectively. The radical quenching experiments and electron spin resonance (ESR) analysis suggested that both non-radical pathway and radical pathway advanced SMX degradation. SMX was oxidized by sulfate radicals (SO4•-), hydroxyl radicals (•OH) and singlet oxygen (1O2), and SO4•- acted as the main active species. MgFeO@BC exhibits a higher current density, and therefore, a higher electron migration rate and redox capacity. Due to the large number of available binding sites on the surface of MgFeO@BC and the low amount of ion leaching during the catalytic reaction, the system has good anti-interference ability and stability. Finally, the intermediates of SMX were detected.
Keywords: biochar-based catalysts; nonradical pathway; peroxymonosulfate; sulfate radicals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Fe@N Co-Doped Biochar for the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole: The Key Role of Pyrrolic N.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 30;25(19):10528. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910528. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408859 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Rice-Husk-Derived Biochar (RBC) for the Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole: The Key Role of Hydroxyl Groups.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 29;25(21):11582. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111582. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519134 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the efficient removal and mechanism of NiFeAl-LDH with abundant hydroxyl to activate peroxymonosulfate for sulfamethoxazole wastewater.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2025 Jan 15;678(Pt A):920-936. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2024.08.171. Epub 2024 Aug 28. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2025. PMID: 39226833
-
Activation of peroxymonosulfate by Fe,N co-doped walnut shell biochar for the degradation of sulfamethoxazole: Performance and mechanisms.Environ Pollut. 2024 Aug 15;355:124018. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.124018. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Environ Pollut. 2024. PMID: 38697252
-
Progress of metal-loaded biochar-activated persulfate for degradation of emerging organic contaminants.Water Sci Technol. 2024 Aug;90(3):824-843. doi: 10.2166/wst.2024.256. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Water Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39141037 Review.
References
-
- Abellán M.N., Bayarri B., Giménez J., Costa J. Photocatalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole in aqueous suspension of TiO2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007;74:233–241. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.02.017. - DOI
-
- Wu D., Sui Q., Yu X., Zhao W., Li Q., Fatta-Kassinos D., Lyu S. Identification of indicator PPCPs in landfill leachates and livestock wastewaters using multi-residue analysis of 70 PPCPs: Analytical method development and application in Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021;753:141653. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141653. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xu M., Li J., Yan Y., Zhao X., Yan J., Zhang Y., Lai B., Chen X., Song L. Catalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole through peroxymonosulfate activated with expanded graphite loaded CoFe2O4 particles. Chem. Eng. J. 2019;369:403–413. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.075. - DOI
-
- Xu Y., Liu S., Wang M., Zhang J., Ding H., Song Y., Zhu Y., Pan Q., Zhao C., Deng H. Thiourea-assisted one-step fabrication of a novel nitrogen and sulfur co-doped biochar from nanocellulose as metal-free catalyst for efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021;416:125796. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125796. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2019YFC0408500/National Key R&D Program of China
- 201903a07020009/Major Science and Technology Projects of Anhui Province
- 202003a07020004/Major Science and Technology Projects of Anhui Province
- J2020K07/Hefei independent innovation policy loan transfer subsidy project
- 52300016/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

