Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of Gene Family of Carbohydrate-Binding Modules in Ustilago crameri
- PMID: 39519340
- PMCID: PMC11546739
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252111790
Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of Gene Family of Carbohydrate-Binding Modules in Ustilago crameri
Abstract
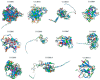
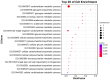
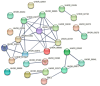
Ustilago crameri is a pathogenic basidiomycete fungus that causes foxtail millet kernel smut (FMKS), a devastating grain disease in most foxtail millet growing regions of the world. Carbohydrate-Binding Modules (CBMs) are one of the important families of carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) in fungi and play a crucial role in fungal growth and development, as well as in pathogen infection. However, there is little information about the CBM family in U. crameri. Here, 11 CBM members were identified based on complete sequence analysis and functional annotation of the genome of U. crameri. According to phylogenetic analysis, they were divided into six groups. Gene structure and sequence composition analysis showed that these 11 UcCBM genes exhibit differences in gene structure and protein motifs. Furthermore, several cis-regulatory elements involved in plant hormones were detected in the promoter regions of these UcCBM genes. Gene ontology (GO) enrichment and protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis showed that UcCBM proteins were involved in carbohydrate metabolism, and multiple partner protein interactions with UcCBM were also detected. The expression of UcCBM genes during U. crameri infection is further clarified, and the results indicate that several UcCBM genes were induced by U. crameri infection. These results provide valuable information for elucidating the features of U. crameri CBMs' family proteins and lay a crucial foundation for further research into their roles in interactions between U. crameri and foxtail millet.
Keywords: CBM; Ustilago crameri; foxtail millet; pathogenicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Integrated Genome Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis Identifies Candidate Pathogenicity Genes from Ustilago crameri.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Jan 21;10(1):82. doi: 10.3390/jof10010082. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38276028 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Sequence Resource of Ustilago crameri, a Fungal Pathogen Causing Millet Smut Disease of Foxtail Millet.Plant Dis. 2023 Feb;107(2):546-548. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-06-22-1439-A. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Plant Dis. 2023. PMID: 36600474 No abstract available.
-
Whole Genome Identification and Biochemical Characteristics of the Tilletia horrida Cytochrome P450 Gene Family.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 28;25(19):10478. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910478. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408807 Free PMC article.
-
Ustilago maydis effectors and their impact on virulence.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017 Jul;15(7):409-421. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2017.33. Epub 2017 May 8. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28479603 Review.
-
A genome-based analysis of amino acid metabolism in the biotrophic plant pathogen Ustilago maydis.Fungal Genet Biol. 2008 Aug;45 Suppl 1:S77-87. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2008.05.006. Epub 2008 May 21. Fungal Genet Biol. 2008. PMID: 18579420 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of Carbohydrate-Binding Modules in Colletotrichum graminicola.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 22;26(3):919. doi: 10.3390/ijms26030919. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940689 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

