Nrf2 Deficiency Exacerbates the Decline in Swallowing and Respiratory Muscle Mass and Function in Mice with Aspiration Pneumonia
- PMID: 39519380
- PMCID: PMC11546094
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252111829
Nrf2 Deficiency Exacerbates the Decline in Swallowing and Respiratory Muscle Mass and Function in Mice with Aspiration Pneumonia
Abstract
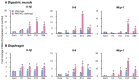
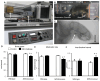
Aspiration pneumonia exacerbates swallowing and respiratory muscle atrophy. It induces respiratory muscle atrophy through three steps: proinflammatory cytokine production, caspase-3 and calpain, and then ubiquitin-proteasome activations. In addition, autophagy induces swallowing muscle atrophy. Nrf2 is the central detoxifying and antioxidant gene whose function in aspiration pneumonia is unclear. We explored the role of Nrf2 in aspiration pneumonia by examining swallowing and respiratory muscle mass and function using wild-type and Nrf2-knockout mice. Pepsin and lipopolysaccharide aspiration challenges caused aspiration pneumonia. The swallowing (digastric muscles) and respiratory (diaphragm) muscles were isolated. Quantitative RT-PCR and Western blotting were used to assess their proteolysis cascade. Pathological and videofluoroscopic examinations evaluated atrophy and swallowing function, respectively. Nrf2-knockouts showed exacerbated aspiration pneumonia compared with wild-types. Nrf2-knockouts exhibited more persistent and intense proinflammatory cytokine elevation than wild-types. In both mice, the challenge activated calpains and caspase-3 in the diaphragm but not in the digastric muscles. The digastric muscles showed extended autophagy activation in Nrf2-knockouts compared to wild-types. The diaphragms exhibited autophagy activation only in Nrf2-knockouts. Nrf2-knockouts showed worsened muscle atrophies and swallowing function compared with wild-types. Thus, activation of Nrf2 may alleviate inflammation, muscle atrophy, and function in aspiration pneumonia, a major health problem for the aging population, and may become a therapeutic target.
Keywords: Nrf2; aspiration pneumonia; muscle atrophy; respiratory muscles; swallowing muscles.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Peerada Ngamsnae is employed by the company MDPI. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

